Introduction: Why Hidden IPTV Encoder Problems Can Ruin Your Streaming in 2025
An IPTV encoder can make or break your streaming quality, yet most providers focus only on the obvious issues while missing critical hidden problems that silently sabotage their broadcasts. While dropped connections and pixelated video are immediately noticeable, the most dangerous IPTV encoder issues operate beneath the surface, gradually eroding viewer experience and damaging your reputation before you even realize what’s happening.
In 2025, the streaming landscape has become increasingly competitive, with viewers expecting flawless quality across multiple devices and network conditions. Hidden streaming issues can cost you thousands of subscribers, damage brand trust, and create cascading problems that are exponentially more expensive to fix than prevent. Unlike obvious IPTV encoder failures that trigger immediate alerts, these six hidden problems often manifest as subtle degradation patterns that can persist for weeks or months before being detected. IPTV encoder.
The challenge with IPTV encoder troubleshooting is that these hidden issues often present symptoms that mirror network problems, making diagnosis difficult without proper monitoring tools and systematic analysis. This comprehensive guide reveals six critical but overlooked IPTV encoder problems that could be undermining your streaming operation right now, along with practical solutions to identify, fix, and prevent each issue.
Table of Contents
Problem 1: Inconsistent Bitrate Handling Under High Load
The Hidden Issue
Most IPTV providers test their IPTV encoder setups during off-peak hours with limited concurrent streams, missing a critical vulnerability that only emerges under high load conditions. When your IPTV encoder faces peak demand, inconsistent bitrate handling creates a cascade of quality issues that appear randomly across your viewer base. IPTV encoder.
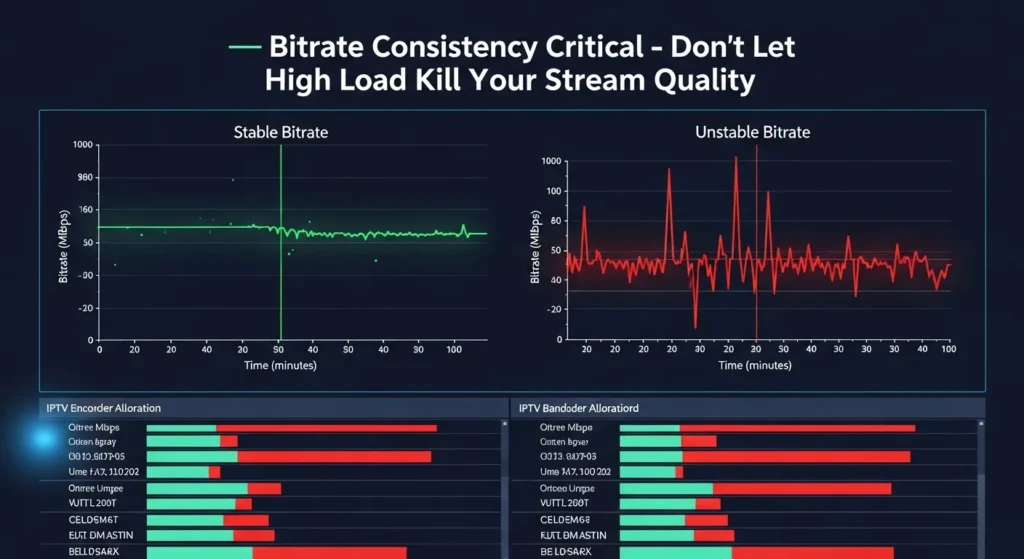
This hidden streaming issue manifests as intermittent buffering for some viewers while others experience perfect quality from the same source. The problem stems from inadequate bitrate allocation algorithms that can’t properly distribute bandwidth when multiple streams compete for resources. Unlike total encoder failure, this creates inconsistent viewer experiences that are difficult to troubleshoot and often blamed on “network issues.” IPTV encoder.
The most insidious aspect of this problem is that it creates viewer churn without obvious cause. Affected viewers experience degraded quality during your busiest periods – exactly when you can least afford to lose audience engagement. Many providers discover this issue only after significant subscriber complaints during major events or peak viewing times. IPTV encoder.
The Fix: Optimizing Encoder Settings and Bandwidth Allocation
Implementing proper bitrate management requires a three-pronged approach focusing on configuration, monitoring, and scaling strategies.
Configuration Optimization: Configure your IPTV encoder with adaptive bitrate ladders that include sufficient headroom for peak loads. Set your primary bitrate to 75% of available bandwidth rather than the typical 85-90%, providing buffer capacity for demand spikes. Implement proper GOP (Group of Pictures) structure with I-frame intervals optimized for your specific content type – sports and fast-action content requires more frequent I-frames than static programming. IPTV encoder.
Load Balancing Implementation: Deploy multiple IPTV encoder instances with intelligent load distribution rather than relying on a single high-capacity unit. This approach prevents bottlenecks and provides redundancy during maintenance or unexpected failures. Configure automatic stream migration protocols that can redistribute load seamlessly when individual encoders approach capacity limits. IPTV encoder.
Real-Time Monitoring: Establish continuous monitoring of bitrate consistency across all output streams. Implement alerting systems that trigger when bitrate variance exceeds 10% of target values for more than 30 seconds. This early warning system allows proactive intervention before viewer impact occurs.
Problem 2: Poor Heat Management Leading to Performance Throttling

The Hidden Issue
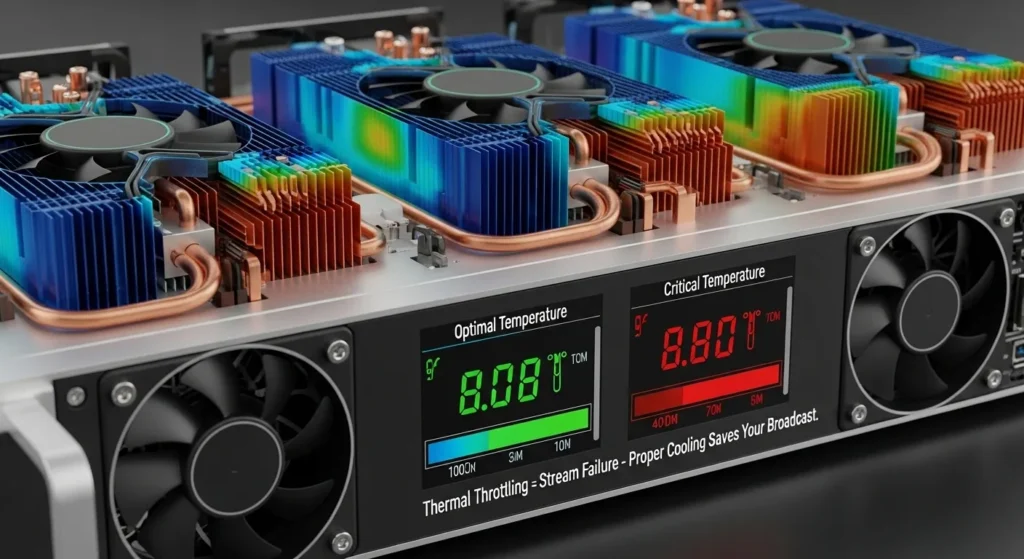
Encoder overheating represents one of the most overlooked yet critical threats to streaming reliability in 2025. Unlike sudden hardware failures, thermal throttling creates gradual performance degradation that’s often attributed to software issues or network problems rather than hardware thermal stress. IPTV encoder.
Modern hardware encoders generate significant heat during operation, and inadequate cooling solutions cause processors to automatically reduce performance to prevent damage. This thermal throttling typically reduces encoding efficiency by 15-30%, creating subtle quality degradation that manifests as increased compression artifacts, higher latency, and reduced frame rate consistency. IPTV encoder.
The challenge with thermal issues is their progressive nature. Initial symptoms include slight increases in encoding latency and occasional frame drops that seem random and intermittent. As thermal stress accumulates, performance degradation accelerates, but the gradual decline makes it difficult to pinpoint the root cause without proper thermal monitoring.
The Fix: Proper Cooling Solutions and Thermal Monitoring
Effective thermal management requires both preventive infrastructure and active monitoring systems to maintain optimal encoder performance. IPTV encoder.
Infrastructure Solutions: Install dedicated cooling systems sized for peak thermal loads rather than average operating temperatures. Hardware encoders should maintain operating temperatures below 70°C (158°F) for optimal performance, with cooling capacity designed for 130% of maximum heat generation. Implement proper airflow design with intake and exhaust fans positioned to create consistent air circulation around all heat-generating components. IPTV encoder.
Consider liquid cooling solutions for high-density encoder deployments where air cooling proves insufficient. Liquid cooling provides more consistent temperature control and operates more quietly than high-speed fans, which can interfere with audio production environments. IPTV encoder.
Monitoring and Alerting: Deploy thermal monitoring sensors at critical points throughout your encoder infrastructure. Monitor CPU, GPU, and ambient temperatures continuously, with automated alerts when temperatures exceed safe thresholds. Implement thermal trend analysis that can predict overheating before critical thresholds are reached, allowing proactive intervention. IPTV encoder.
Maintenance Protocols: Establish regular cleaning schedules for cooling systems, as dust accumulation significantly reduces cooling efficiency. Implement thermal paste replacement schedules for processors, typically every 12-18 months depending on operating conditions. Document thermal performance baselines to identify degradation trends before they impact streaming quality. IPTV encoder.
Problem 3: Limited Protocol Compatibility Reducing Audience Reach
The Hidden Issue
Protocol compatibility limitations represent a silent barrier to audience growth that many IPTV providers discover only after losing potential viewers. While your encoder might produce perfect streams for your primary target devices, hidden incompatibilities with emerging devices and platforms can silently exclude significant portions of your potential audience.

This issue becomes particularly problematic as viewer device diversity increases. Smart TVs, mobile devices, set-top boxes, and streaming sticks each have specific protocol requirements and capabilities. An IPTV encoder that only supports a limited range of protocols creates invisible barriers that prevent certain devices from accessing your content, resulting in missed revenue opportunities and reduced market penetration.
The most challenging aspect of protocol compatibility issues is their inconsistency across device generations and manufacturers. A configuration that works perfectly with current-generation devices might fail with older models or emerging platforms, creating sporadic access problems that are difficult to diagnose and resolve.
The Fix: Ensuring Multi-Protocol Output and Backward Compatibility
Comprehensive protocol support requires strategic encoder selection and configuration optimization that addresses both current and future compatibility requirements.
Multi-Protocol Configuration: Configure your encoder to simultaneously output multiple protocol streams optimized for different device categories. Implement HLS (HTTP Live Streaming) for iOS and Safari browsers, DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP) for Android and modern web browsers, and RTMP for legacy flash-based systems and broadcast applications.
Ensure proper segment duration configuration for each protocol – HLS segments should be 6-10 seconds for optimal compatibility, while DASH segments can be shorter (2-4 seconds) for reduced latency. Configure appropriate playlist depths to balance startup time with seeking capabilities across different devices.
Backward Compatibility Strategies: Maintain support for older protocol versions while implementing newer standards. This dual-stream approach ensures maximum device compatibility without sacrificing the benefits of modern protocols. Implement automatic protocol detection and selection based on user agent strings and device capabilities.
Testing and Validation: Establish comprehensive device testing protocols that cover major device categories and operating system versions. Create automated testing suites that verify stream compatibility across different protocols and device types. Implement regular compatibility audits to identify and address emerging compatibility issues before they impact viewers.
Problem 4: Weak Error Recovery in Unstable Network Conditions
The Hidden Issue
Network instability represents an inevitable challenge in IPTV delivery, yet many encoders lack robust streaming error recovery mechanisms that can maintain quality during temporary network disruptions. This vulnerability becomes a critical hidden problem when encoders fail to properly handle packet loss, jitter, or brief connection interruptions.
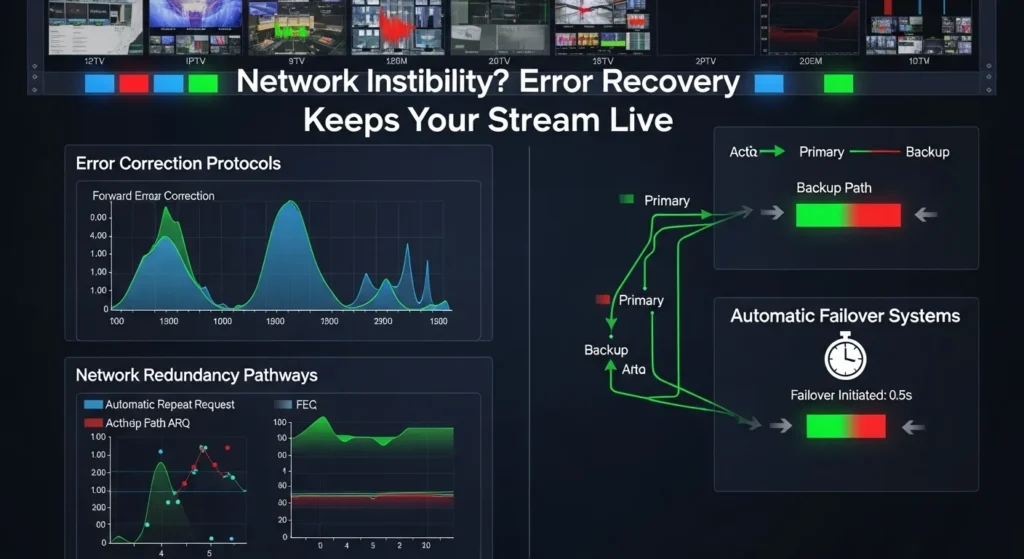
Weak error recovery manifests as complete stream failures during minor network hiccups that should be transparently handled. Instead of gracefully degrading quality or buffering through brief disruptions, poorly configured encoders drop connections entirely, forcing viewers to manually restart streams and creating frustrating user experiences.
The complexity of modern network environments makes this problem particularly challenging. Content delivery networks, edge servers, and last-mile connections each introduce potential points of failure. An encoder that performs flawlessly in controlled test environments may fail catastrophically when facing real-world network variability and unexpected disruption patterns. IPTV encoder.
The Fix: Leveraging Error Correction Protocols and Redundancy
Robust error recovery requires implementing multiple layers of protection that can handle various types of network disruptions without impacting viewer experience. IPTV encoder.
Error Correction Implementation: Configure Forward Error Correction (FEC) protocols that can recover lost packets without requiring retransmission. FEC adds redundant data to streams, allowing decoders to reconstruct missing information when packet loss occurs. Implement adaptive FEC that adjusts redundancy levels based on detected network conditions.
Deploy Automatic Repeat reQuest (ARQ) mechanisms for critical stream components while balancing latency requirements. ARQ protocols can request retransmission of critical packets while maintaining acceptable latency for live streaming applications. IPTV encoder.
Network Redundancy Strategies: Implement multiple network paths for critical streams, allowing automatic failover when primary connections experience problems. Configure bonding protocols that can aggregate multiple network connections for increased bandwidth and redundancy.
Deploy geographically distributed encoder instances that can seamlessly take over stream delivery when primary locations experience network issues. This geographic redundancy protects against regional network outages and routing problems.
Buffer Management: Optimize buffer configurations to balance startup latency with error recovery capabilities. Implement adaptive buffering that can temporarily increase buffer depth when network instability is detected, providing additional protection against disruptions while maintaining acceptable latency during stable conditions. IPTV encoder.
Problem 5: Lack of Firmware Updates and Security Patches
The Hidden Issue
Firmware maintenance represents one of the most critical yet overlooked aspects of IPTV encoder management. Many providers deploy encoder systems and then neglect ongoing firmware updates, creating security vulnerabilities and missing performance improvements that accumulate over time. IPTV encoder.
This hidden problem manifests in multiple ways: degraded performance as newer streaming standards emerge, security vulnerabilities that expose your infrastructure to attacks, and compatibility issues with evolving CDN and platform requirements. Unlike hardware failures that trigger immediate attention, firmware neglect creates gradual degradation that’s often attributed to other causes.
The security implications of outdated firmware are particularly concerning in 2025’s threat landscape. Encoder systems often contain embedded web servers, network interfaces, and remote management capabilities that can become attack vectors when security patches aren’t applied regularly. These vulnerabilities can provide attackers with access to your entire streaming infrastructure. IPTV encoder.
The Fix: Establishing Update Schedules and Maintenance Logs
Comprehensive firmware management requires systematic approaches to updates, testing, and documentation that ensure security and performance without introducing operational risks. IPTV encoder.
Update Scheduling Protocols: Establish regular firmware update schedules that balance security needs with operational stability. Implement a monthly review process for critical security patches and quarterly updates for performance and feature enhancements. Create separate update tracks for production and development systems, allowing thorough testing before deploying updates to live environments. IPTV encoder.
Develop rollback procedures that can quickly restore previous firmware versions if updates introduce unexpected problems. Maintain complete configuration backups before any firmware modifications, ensuring rapid recovery if issues arise.
Security Monitoring: Implement continuous security monitoring that tracks known vulnerabilities affecting your encoder models. Subscribe to manufacturer security bulletins and industry threat intelligence feeds that provide early warning of emerging risks. Establish priority protocols for critical security patches that require immediate deployment.
Testing and Validation: Create comprehensive testing protocols that validate encoder functionality after firmware updates. Test all critical features including stream output quality, protocol compatibility, remote management functionality, and integration with existing monitoring systems. Document test results and maintain performance baselines that can identify regression issues. IPTV encoder.
Documentation and Logging: Maintain detailed logs of all firmware updates including versions, deployment dates, and validation results. Create systematic documentation of encoder configurations that can accelerate troubleshooting and ensure consistent deployments across multiple systems. IPTV encoder.
Problem 6: No Future-Ready Support for Emerging Formats (HEVC, AV1)
The Hidden Issue
Codec evolution represents a significant challenge for long-term streaming viability, yet many IPTV providers select encoders without considering future-proof encoding capabilities. This shortsightedness creates hidden obsolescence risks that can require expensive infrastructure replacements as new codecs become standard.
The transition to next-generation codecs like HEVC (H.265) and AV1 offers significant bandwidth savings – up to 50% compared to H.264 – but requires encoder hardware and software that can adapt to these evolving standards. Providers using encoders without upgradeable codec support face difficult choices: accept reduced efficiency and higher bandwidth costs, or undertake expensive hardware replacements.
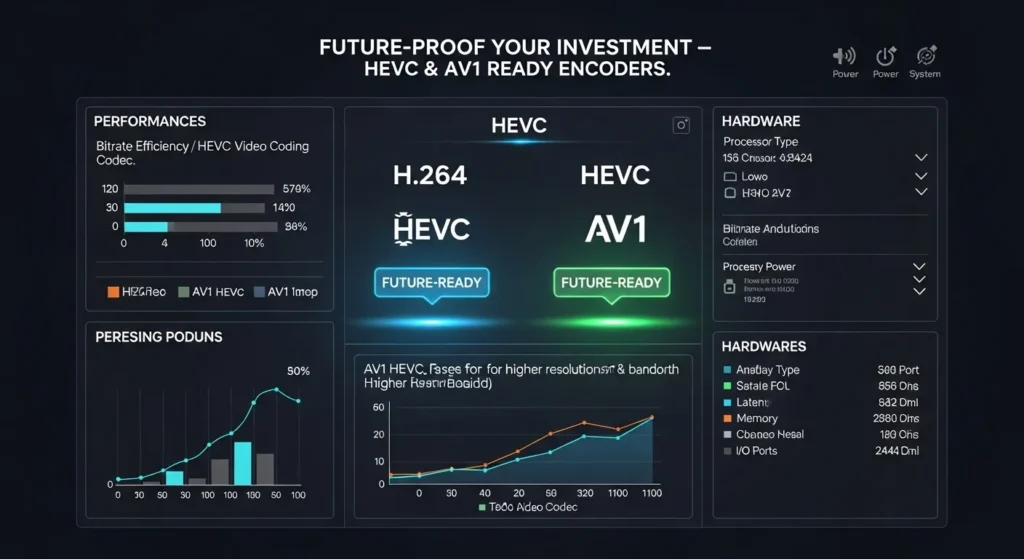
This problem compounds over time as newer codecs become market expectations rather than optional enhancements. Viewers accessing content through modern devices increasingly expect HEVC support, while AV1 adoption accelerates driven by major platforms and improved decoder availability. Encoders locked into older codecs become competitive disadvantages.
The Fix: Choosing Encoders with Upgradeable Firmware and Codec Support
Future-proofing your encoding infrastructure requires strategic hardware selection and configuration that can adapt to evolving codec requirements.
Hardware Selection Criteria: Select encoder systems with documented codec upgrade paths and sufficient processing headroom for next-generation formats. HEVC encoding requires approximately 2-3x more processing power than H.264, while AV1 encoding demands even higher computational resources. Choose hardware platforms that can handle these increased requirements without complete replacement.
Prioritize encoders with FPGA-based processing or software-defined encoding capabilities that can be updated to support new codecs through firmware updates. Avoid hardware-locked systems that require physical replacement for codec upgrades.
Multi-Codec Deployment Strategies: Implement parallel encoding strategies that can simultaneously output multiple codec versions of the same content. This approach allows gradual migration to newer codecs while maintaining compatibility with legacy devices. Configure automatic codec selection based on device capabilities and bandwidth availability. IPTV encoder.
Deploy adaptive bitrate ladders that include multiple codec options, allowing players to select optimal formats based on device capabilities and network conditions. This approach maximizes quality while ensuring universal compatibility.
Migration Planning: Develop systematic migration plans that can transition to newer codecs without service disruption. Implement A/B testing protocols that can validate new codec performance across different device types and network conditions before full deployment.
Create performance monitoring that tracks codec efficiency, quality metrics, and device compatibility across your viewer base. Use this data to optimize migration timing and identify potential compatibility issues before they impact significant numbers of viewers.
Solutions Checklist: How to Stay Ahead of Encoder Problems
Immediate Actions (Within 30 Days)
- Thermal Monitoring: Install temperature sensors and establish baseline thermal performance metrics for all encoder hardware
- Firmware Audit: Document current firmware versions across all encoders and identify available updates
- Protocol Testing: Verify stream compatibility across major device categories and document any identified gaps
- Load Testing: Conduct peak load simulations to identify bitrate handling limitations under stress conditions
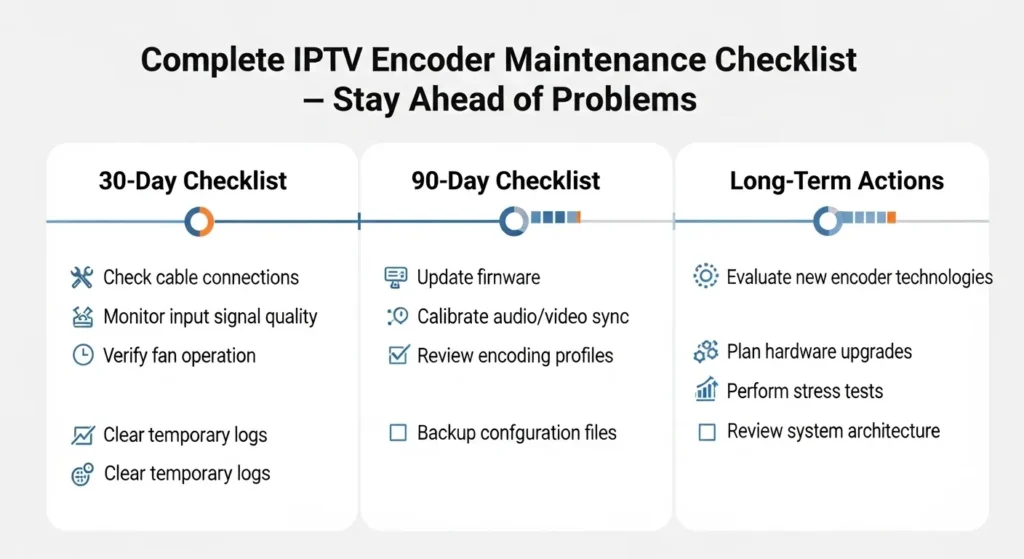
Medium-Term Improvements (30-90 Days)
- Cooling Upgrades: Implement proper cooling solutions for any encoders operating above optimal temperature ranges
- Error Recovery Configuration: Deploy and configure FEC protocols and network redundancy for critical streams
- Multi-Codec Planning: Evaluate encoder capabilities for HEVC/AV1 support and develop migration timelines
- Monitoring Systems: Implement comprehensive monitoring that tracks all six hidden problem areas with automated alerting
Long-Term Strategic Planning (90+ Days)
- Infrastructure Scaling: Plan encoder infrastructure expansion that addresses identified bottlenecks and future growth requirements
- Technology Roadmap: Develop 2-year technology adoption plans that align with codec evolution and industry standards
- Disaster Recovery: Implement geographic redundancy and comprehensive failover capabilities for mission-critical streams
- Performance Optimization: Establish continuous improvement processes that can proactively identify and address emerging issues
Ongoing Maintenance Protocols
- Weekly: Review thermal and performance monitoring alerts, validate stream quality across device types
- Monthly: Apply critical security patches, conduct comprehensive protocol compatibility testing
- Quarterly: Perform load testing, update firmware for performance enhancements, review and update documentation
- Annually: Conduct comprehensive infrastructure assessment, evaluate technology upgrade requirements, validate disaster recovery procedures
Conclusion: Protecting Your Streaming Quality in 2025
The six hidden IPTV encoder problems outlined in this guide represent critical threats to streaming quality and business success that operate below the surface of obvious technical issues. Unlike hardware failures or network outages that trigger immediate attention, these hidden problems create gradual degradation patterns that can persist for months while silently damaging viewer experience and competitive positioning.
Addressing these challenges requires proactive monitoring, systematic maintenance, and strategic planning that extends beyond reactive troubleshooting. The solutions presented here provide actionable frameworks for identifying, resolving, and preventing each category of hidden encoder problems before they impact your audience.

The streaming industry’s rapid evolution in 2025 demands encoder infrastructure that can adapt to changing requirements while maintaining consistent quality and reliability. By implementing comprehensive thermal management, robust error recovery, multi-protocol compatibility, and future-ready codec support, you create resilient streaming infrastructure that can thrive in competitive markets.
Success in modern IPTV delivery requires treating your encoder infrastructure as a dynamic system that needs continuous attention and optimization rather than static equipment that can be deployed and forgotten. The providers who implement these preventive measures will maintain competitive advantages through superior streaming quality, while those who ignore these hidden problems will face increasingly expensive reactive solutions and potentially irrecoverable audience losses.
Taking action on these six hidden problems now protects your streaming investment, ensures viewer satisfaction, and positions your operation for sustainable growth in the evolving IPTV landscape. The choice between proactive prevention and reactive crisis management will determine which providers succeed in 2025’s competitive streaming environment.





