Introduction: Why the Right IPTV Encoder Encoders Matters in 2025
An IPTV encoder encoders is the backbone of any high-quality streaming setup, serving as the critical bridge between your raw video content and your audience’s viewing experience. In today’s competitive streaming landscape, the difference between a professional-grade broadcast and amateur-level content often comes down to one crucial decision: selecting the right encoding hardware or software for your specific workflow.
The stakes have never been higher for IPTV providers, broadcasters, and content creators. Viewers expect crystal-clear video quality, minimal buffering, and seamless playback across multiple devices and network conditions. When your IPTV encoder encoders fails to deliver on these expectations, the consequences extend far beyond technical frustration. Poor encoding choices lead to viewer churn, increased support costs, and damaged brand reputation that can take months or years to rebuild. IPTV encoder encoders.
Understanding how to evaluate and select the optimal live streaming encoder has become an essential skill for anyone serious about delivering professional-grade IPTV content. This comprehensive guide breaks down the complex world of video signal capture, real-time encoding, and multi-protocol broadcast into actionable insights that will help you make informed decisions about your streaming infrastructure.
Whether you’re managing a small-scale content creation operation or overseeing enterprise-level broadcast systems, the seven proven tips outlined in this guide will help you navigate the technical complexities while avoiding costly mistakes that plague many IPTV deployments. IPTV encoder encoders.
Table of Contents
Understanding IPTV Encoders: Hardware vs. Software Solutions

Before diving into specific selection criteria, it’s essential to understand the fundamental differences between hardware and software-based encoding solutions. This distinction forms the foundation of every other decision you’ll make about your streaming infrastructure. IPTV encoder encoders.
Hardware IPTV Encoders: The Dedicated Approach
Hardware encoders are purpose-built devices designed specifically for video signal capture and real-time encoding. These dedicated units typically feature specialized chips called Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) or Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) that handle encoding tasks with remarkable efficiency. Think of hardware encoders as the sports cars of the encoding world – they’re built for one specific task and excel at it.
The primary advantage of hardware encoders lies in their predictable performance characteristics. When you connect a video source to a hardware encoder, the encoding process operates independently of other system resources. This isolation means your encoding quality remains consistent regardless of what else might be happening in your broadcasting environment. Hardware encoders also tend to introduce lower latency, making them ideal for applications where real-time interaction matters, such as live sports broadcasts or interactive streaming events.
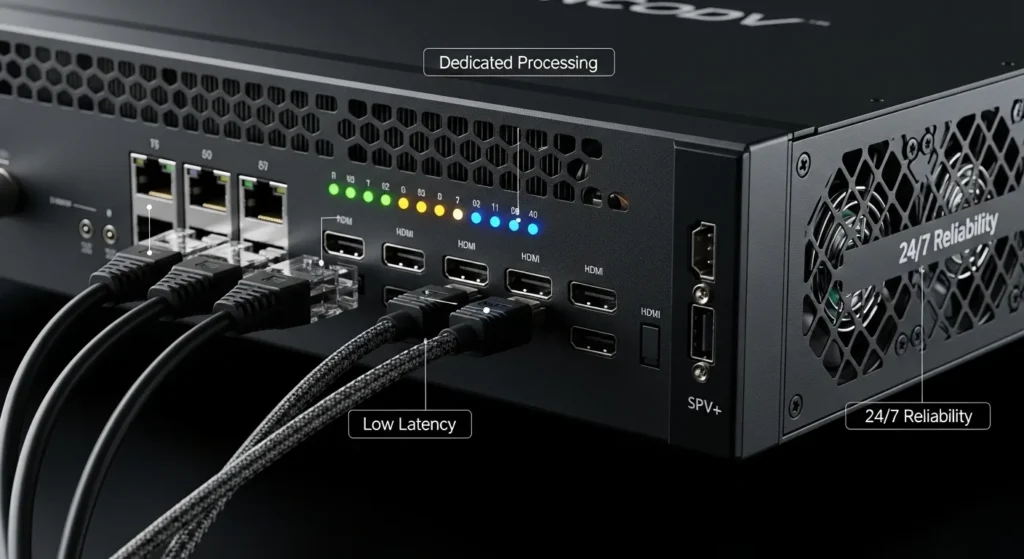

However, hardware solutions come with trade-offs that extend beyond their typically higher upfront costs. Upgrading codec support or adding new protocols often requires purchasing entirely new hardware, which can make long-term total cost of ownership surprisingly high. Additionally, hardware encoders generally offer less flexibility when it comes to custom configurations or integration with complex workflow automation systems. IPTV encoder encoders.
Software IPTV Encoders: The Flexible Alternative
Software encoders run on general-purpose computing hardware, leveraging the CPU, GPU, or specialized acceleration cards to handle encoding tasks. Modern software encoders have evolved significantly, with many now supporting hardware acceleration through technologies like Intel Quick Sync, NVIDIA NVENC, or AMD VCE. This hybrid approach combines the flexibility of software with much of the performance traditionally associated with dedicated hardware.
The compelling advantage of software encoders lies in their adaptability. Need to add support for a new streaming protocol? A software update handles it. Want to integrate custom analytics or automated quality monitoring? Software solutions typically offer robust APIs and integration options. For organizations that need to handle multiple simultaneous streams or frequently change their encoding parameters, software solutions often prove more cost-effective in the long run.
The challenge with software encoders comes from their dependency on the underlying computing infrastructure. A software encoder competing for system resources with other applications can experience performance degradation or unexpected interruptions. This variability requires more sophisticated monitoring and management compared to dedicated hardware solutions. IPTV encoder encoders.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Workflow
The decision between hardware and software encoding isn’t always straightforward, and many successful IPTV operations use hybrid approaches that leverage the strengths of both technologies. For mission-critical applications where consistency trumps flexibility, hardware encoders often provide the reliability and predictable performance that justifies their higher costs. Conversely, for dynamic environments where requirements change frequently or where budget constraints limit hardware investments, software encoders offer compelling value propositions. IPTV encoder encoders.
Consider your organization’s technical expertise when making this choice. Hardware encoders typically require less ongoing management once properly configured, while software solutions often demand more hands-on attention but provide greater control over the encoding process. The best choice aligns with your team’s capabilities and your specific operational requirements.
Key Features to Look For in a Modern IPTV Encoder
Modern IPTV encoders have evolved far beyond simple video compression tools, incorporating sophisticated features that can make or break your streaming success. Understanding which features matter most for your specific use case helps you avoid both over-engineering and under-specification. IPTV encoder encoders.
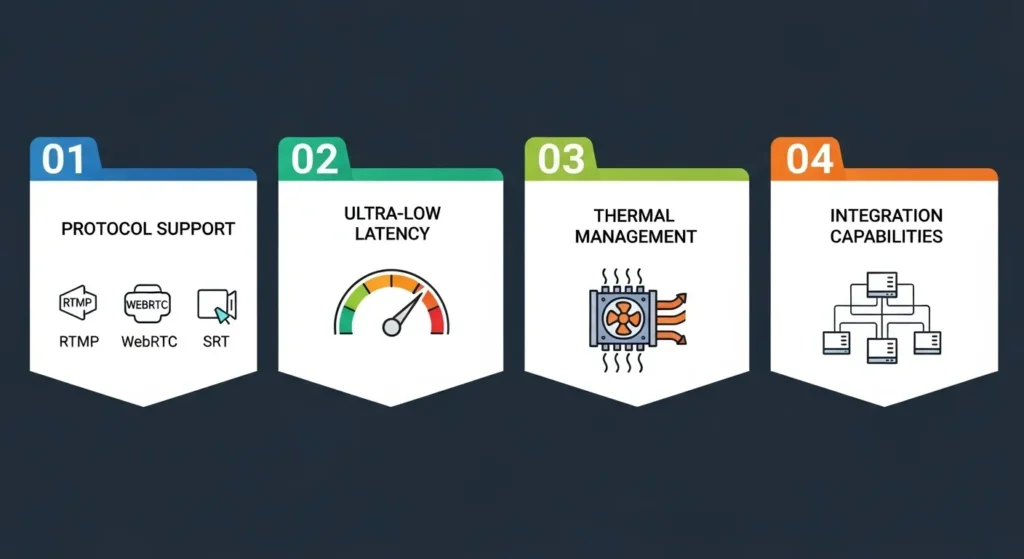
Comprehensive Protocol Support
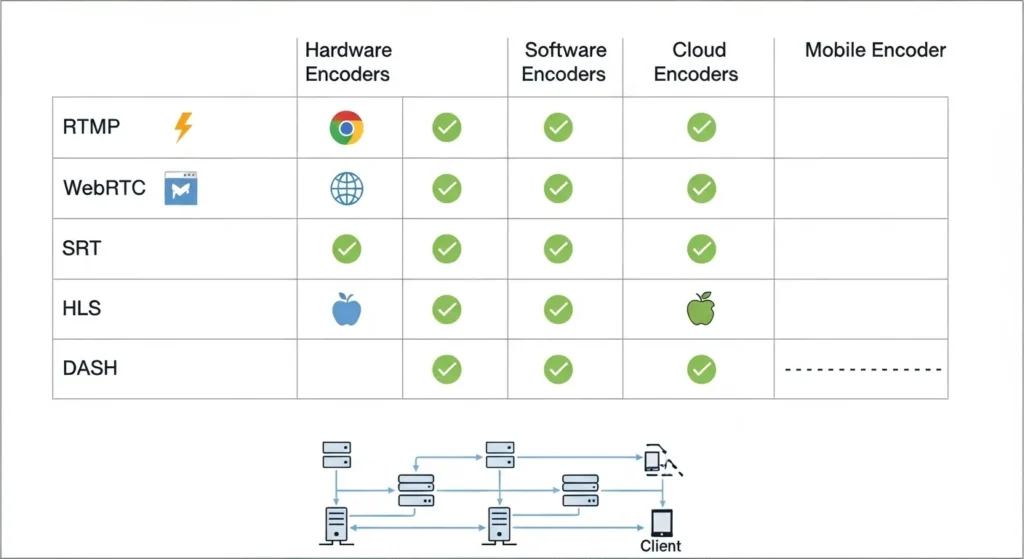
Today’s streaming ecosystem demands flexibility in output formats and delivery protocols. Your IPTV encoder encoders should support the full spectrum of modern streaming protocols, including RTMP for traditional streaming platforms, SRT for reliable low-latency transmission over unreliable networks, and HLS for adaptive bitrate streaming to diverse client devices. IPTV encoder encoders.
The most valuable encoders go beyond basic protocol support to offer advanced features within each protocol. For RTMP implementations, look for encoders that support authentication, SSL encryption, and automatic reconnection capabilities. SRT support should include caller and listener modes, along with configurable latency and bandwidth overhead parameters. HLS implementations should offer variable segment durations, multiple quality tiers, and proper metadata handling for seamless player compatibility. IPTV encoder encoders.
Ultra-Low Latency Performance
Latency performance has become increasingly critical as streaming applications move beyond traditional broadcast models toward interactive and real-time experiences. Understanding the different sources of latency in your encoding pipeline helps you make informed decisions about acceptable trade-offs between quality, reliability, and responsiveness.
Encoding latency represents just one component of your total end-to-end latency, but it’s often the most controllable element in your streaming chain. Modern encoders should offer sub-second encoding latency for applications requiring real-time interaction, while still providing options for higher-latency modes that prioritize compression efficiency for bandwidth-constrained scenarios. IPTV encoder encoders.
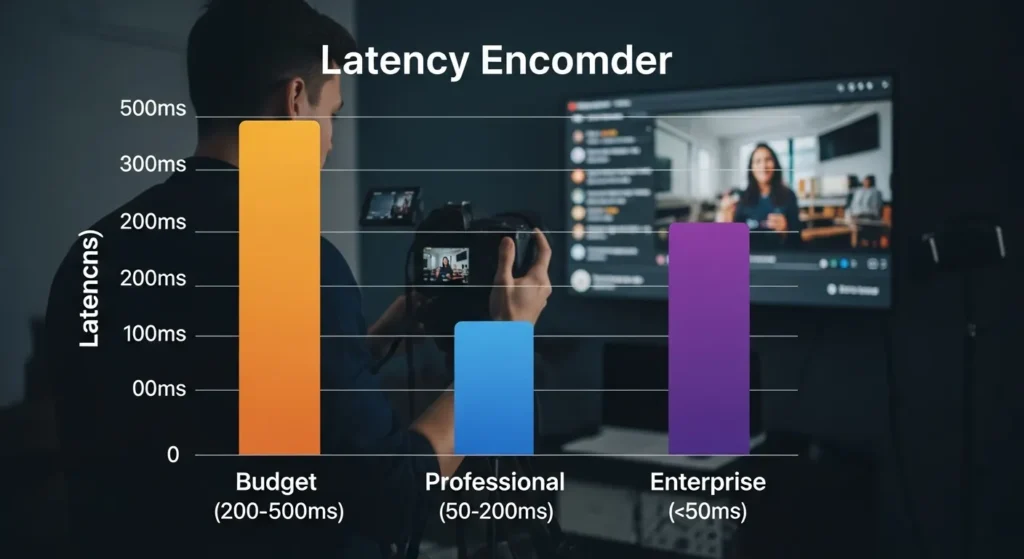
When evaluating latency specifications, pay attention to how manufacturers measure and report these numbers. Some vendors report theoretical minimums under ideal conditions, while others provide more realistic figures that account for real-world variables like network jitter and processing overhead. The most useful latency specifications include both typical and worst-case scenarios under your expected operating conditions. IPTV encoder encoders.
Thermal Management and Reliability Engineering
Professional IPTV operations run continuously, often in environments that aren’t optimized for sensitive electronic equipment. Your encoder’s thermal management system directly impacts both its immediate reliability and long-term operational lifespan. Understanding these thermal considerations helps you plan your installation environment and avoid costly failures.
Effective thermal management goes beyond simple fan cooling to include intelligent thermal monitoring, progressive performance scaling under thermal stress, and graceful degradation rather than abrupt failures when thermal limits are reached. The best encoders incorporate multiple temperature sensors throughout the device, providing detailed telemetry that enables proactive maintenance and optimal environmental planning. IPTV encoder encoders.
Consider the acoustic implications of cooling systems, especially for encoders deployed in production environments where noise pollution can disrupt operations. Passive cooling solutions or intelligently managed fan systems that balance thermal performance with acoustic considerations often prove valuable in real-world deployments. IPTV encoder encoders.
Integration and Management Capabilities
Modern IPTV operations increasingly rely on automated workflows and centralized management systems to maintain operational efficiency at scale. Your encoder selection should consider not just the encoding performance, but also how well the device integrates into your broader operational infrastructure. IPTV encoder encoders.
Look for encoders that provide comprehensive management APIs, supporting both configuration changes and real-time monitoring through standard protocols like SNMP or modern REST APIs. The most valuable management implementations provide granular access to operational parameters, enabling custom dashboards, automated alerting, and integration with existing network management systems. IPTV encoder encoders.
Consider the encoder’s support for configuration backup and restoration, especially for deployments involving multiple identical units. Encoders that support configuration templates and bulk deployment procedures can significantly reduce operational overhead while ensuring consistency across your infrastructure.
7 Proven Tips for Choosing the Best IPTV Encoder Encoders
Selecting the optimal IPTV encoder encoders for your specific requirements demands a systematic approach that balances technical performance, operational requirements, and long-term strategic considerations. These seven proven tips distill years of real-world deployment experience into actionable guidance that helps you avoid common pitfalls while identifying solutions that truly fit your needs.
Tip 1: Match Encoder Type to Your Content Workflow
Your content workflow fundamentally determines which encoder architecture will serve you best. Live content creation with unpredictable schedules and varying technical requirements often benefits from the flexibility that software encoders provide. These solutions adapt quickly to changing requirements, support custom configurations, and integrate easily with content management systems and automation tools.
Conversely, scheduled broadcast operations with consistent technical parameters often achieve better results with dedicated hardware encoders. The predictable performance characteristics and reduced management overhead of hardware solutions align well with operations where reliability and consistency outweigh flexibility.
Consider hybrid approaches for complex operations. Many successful IPTV providers use hardware encoders for their primary broadcast streams while maintaining software encoders for backup, overflow, or special event coverage. This strategy provides both the reliability of hardware and the flexibility of software where each is most valuable.
Tip 2: Confirm Supported Protocols and Output Formats
Protocol compatibility extends far beyond simply supporting popular streaming formats. Your encoder must handle the specific implementation details and advanced features that your distribution strategy requires. RTMP support, for example, varies significantly between encoders in terms of authentication methods, SSL implementation, and recovery mechanisms.
Evaluate how well each encoder handles adaptive bitrate streaming if your audience includes viewers on varying connection speeds. The best HLS implementations provide smooth quality transitions, appropriate buffer management, and proper metadata handling that ensures compatibility with diverse player software and device types.
Don’t overlook emerging protocols that might become important to your future operations. SRT adoption continues growing rapidly due to its superior performance over unreliable networks, while WebRTC integration becomes increasingly valuable for interactive streaming applications. Choosing encoders with robust protocol support helps future-proof your investment.
Tip 3: Compare Latency Performance Under Real Conditions
Latency specifications can be misleading when they don’t account for real-world operating conditions. The most meaningful latency comparisons consider your actual content types, network conditions, and quality requirements rather than theoretical minimums under ideal circumstances.
Test encoders using your actual content types whenever possible. Motion-heavy content like sports requires different encoding strategies than relatively static content like news broadcasts, and these differences can significantly impact both latency and quality outcomes. Encoders that perform well with one content type might struggle with others.
Consider the entire latency budget for your streaming pipeline, not just the encoding component. Network transmission, player buffering, and display processing all contribute to the total delay between your source content and viewer experience. Optimizing encoding latency provides limited benefits if other pipeline components introduce larger delays.
Tip 4: Assess Reliability Under Peak Traffic Conditions
Encoder reliability becomes most critical during high-traffic events when the consequences of failure are most severe. Understanding how different encoders handle stress conditions, recover from failures, and maintain performance under load helps you avoid costly outages during important broadcasts.
Evaluate the encoder’s behavior when approaching resource limits. The best encoders provide graceful performance degradation rather than abrupt failures, maintaining basic functionality even when operating beyond their optimal parameters. This characteristic proves invaluable during unexpected traffic spikes or when dealing with higher-than-anticipated resource demands.
Consider the encoder’s recovery mechanisms after network interruptions or other temporary failures. Automatic reconnection capabilities, buffer management during outages, and seamless resumption of encoding operations can mean the difference between minor service hiccups and extended outages that damage viewer confidence.
Tip 5: Evaluate Thermal Management and Power Efficiency
Thermal performance directly impacts both immediate reliability and long-term operational costs. Encoders that run cooler typically last longer, require less maintenance, and can operate in more challenging environmental conditions. Understanding the thermal characteristics of different encoders helps you plan appropriate installation environments and avoid temperature-related failures.
Power efficiency considerations extend beyond environmental responsibility to include practical operational benefits. More efficient encoders generate less heat, reducing cooling requirements and associated costs. They also provide more deployment flexibility, especially for remote or temporary installations where power availability might be limited.
Consider the acoustic implications of thermal management systems, particularly for encoders deployed in production environments. Quiet operation becomes essential when encoders are located near sensitive audio equipment or in environments where noise pollution disrupts operations. IPTV encoder encoders.
Tip 6: Analyze Integration Complexity with Existing Infrastructure
The ease of integrating new encoders into your existing workflow significantly impacts both initial deployment costs and ongoing operational efficiency. Encoders that work seamlessly with your current management systems, monitoring tools, and automation infrastructure provide better long-term value than solutions requiring extensive custom integration work.
Evaluate the quality and completeness of each encoder’s management API. Comprehensive APIs enable custom dashboard creation, automated configuration management, and integration with existing network monitoring systems. The best APIs provide granular access to operational parameters while maintaining security and stability.
Consider the learning curve associated with different encoder platforms. Solutions that align with your team’s existing expertise and preferred management approaches typically result in faster deployments and more effective ongoing operations. The most sophisticated encoder provides limited value if your team struggles to configure and maintain it effectively. IPTV encoder encoders.
Tip 7: Calculate Total Cost of Ownership Beyond Initial Purchase
The true cost of encoder ownership extends far beyond the initial purchase price to include ongoing operational expenses, upgrade costs, and the potential impact of reliability issues on your business operations. A comprehensive total cost analysis provides a more accurate foundation for encoder selection decisions.
Consider ongoing licensing costs for software encoders, particularly those that charge based on concurrent streams or output quality levels. These recurring expenses can significantly impact the long-term cost comparison between different solutions, especially for growing operations where licensing costs scale with usage.
Factor in the costs associated with encoder management and maintenance. Solutions requiring frequent manual intervention or specialized technical expertise for routine operations can generate substantial hidden costs over their operational lifetime. Conversely, encoders with robust automation capabilities and intuitive management interfaces often justify higher initial costs through reduced operational overhead.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Buying an IPTV Encoder Encoders
Understanding the most frequent mistakes in encoder selection helps you avoid costly errors that can compromise your streaming operations. These common pitfalls often stem from focusing too narrowly on specifications while overlooking practical operational considerations. IPTV encoder encoders.

Over-Engineering for Unused Capabilities
Many organizations purchase encoders with extensive feature sets that they never actually use, paying premium prices for capabilities that provide no operational value. This mistake often occurs when decision-makers focus on comprehensive specification sheets rather than carefully analyzing their actual requirements.
The most effective approach involves clearly defining your current needs and realistic growth projections before evaluating encoder options. While some future-proofing makes sense, paying for advanced features that you’re unlikely to use within the encoder’s operational lifetime rarely provides good value. Focus on solutions that excel at your core requirements rather than those offering the longest feature lists.
Underestimating Environmental Requirements
Encoder reliability depends heavily on appropriate installation environments, yet many organizations fail to adequately consider thermal, acoustic, and power requirements during the selection process. This oversight often leads to reliability issues, shortened equipment life, or expensive environmental modifications after deployment.
Carefully evaluate your intended installation environment against each encoder’s environmental specifications. Consider not just the current conditions but also how environmental factors might change over time. Encoders installed in equipment rooms that later become more crowded or in locations where air conditioning might be reduced during off-hours need to handle more challenging thermal conditions than initial assessments might suggest.
Ignoring Protocol Compatibility Details
Basic protocol support often differs significantly from full compatibility with your specific implementation requirements. Many encoders claim to support standard protocols like RTMP or HLS without providing the specific features or implementation quality that your workflow demands.
Test protocol compatibility using your actual streaming infrastructure rather than relying solely on specification sheets. Different RTMP implementations, for example, can vary significantly in their handling of authentication, error recovery, and metadata transmission. These differences can cause compatibility issues that aren’t apparent until after deployment.
Recommended IPTV Encoder Categories for 2025
Understanding the current encoder landscape helps you identify solutions appropriate for different operational scales and budget constraints. Rather than recommending specific models that quickly become outdated, this section focuses on identifying the characteristics that define each category and help you evaluate current options.

Budget-Conscious Solutions for Emerging Operations
Entry-level IPTV encoder encoders have improved dramatically in recent years, offering capabilities that were previously available only in professional-grade equipment. These solutions work well for organizations getting started with IPTV distribution or those with limited technical requirements and budget constraints.
Modern budget encoders typically provide solid basic functionality including support for standard streaming protocols, reasonable encoding quality, and basic management capabilities. However, they often lack advanced features like redundant power supplies, comprehensive management APIs, or support for the latest codec developments. For operations where basic functionality suffices and where some operational limitations are acceptable, these encoders provide excellent value.
When evaluating budget solutions, pay particular attention to thermal management and build quality. Less expensive encoders sometimes compromise on cooling systems or component quality in ways that can impact long-term reliability. Understanding these trade-offs helps you make informed decisions about whether budget solutions meet your reliability requirements. IPTV encoder encoders.
Professional-Grade Solutions for Established Operations
Mid-tier encoders represent the sweet spot for many professional IPTV operations, offering advanced features and robust reliability without the premium pricing of high-end solutions. These encoders typically provide comprehensive protocol support, advanced bitrate configuration options, and professional-grade management capabilities.
Professional encoders often include features like redundant power supplies, comprehensive SNMP support, and robust thermal management systems that enable reliable operation in challenging environments. They typically support advanced encoding features like multiple simultaneous outputs, sophisticated stream redundancy configurations, and integration with professional broadcast equipment. IPTV encoder encoders.
The best professional-grade encoders balance performance, features, and cost in ways that make them suitable for a wide range of IPTV applications. They provide the reliability needed for commercial operations while remaining cost-effective enough for organizations that can’t justify premium pricing for every component in their infrastructure. IPTV encoder encoders. IPTV encoder encoders.
Enterprise Solutions for Mission-Critical Applications
High-end IPTV encoder encoders are designed for organizations where encoder failure would have severe business consequences. These solutions typically include comprehensive redundancy systems, advanced monitoring capabilities, and support for the most demanding performance requirements.
Enterprise encoders often feature hot-swappable components, comprehensive built-in diagnostics, and support for advanced features like automatic failover between redundant encoding paths. They typically provide the most comprehensive management capabilities, including detailed telemetry, predictive failure detection, and integration with enterprise network management systems. IPTV encoder encoders.
The premium pricing of enterprise solutions is justified primarily by their reliability and advanced management capabilities rather than basic encoding performance. For organizations where encoder downtime would result in significant revenue loss or where regulatory requirements demand high reliability, these solutions often provide compelling value despite their higher costs.
Final Verdict: Making a Smart, Future-Proof Choice
Selecting the right IPTV encoder encoders ultimately comes down to matching technical capabilities with your operational requirements while maintaining a realistic perspective on both current needs and future growth. The most successful encoder deployments result from careful analysis of actual requirements rather than pursuit of impressive specifications that don’t translate into operational benefits. IPTV encoder encoders.
The seven tips outlined in this guide provide a framework for systematic encoder evaluation that helps you avoid common pitfalls while identifying solutions that truly fit your needs. Remember that the best encoder for your organization might not be the most expensive or feature-rich option available. Instead, focus on finding solutions that excel at your core requirements while providing reasonable growth headroom for future expansion.
Consider the total operational context when making your final decision. An encoder that integrates seamlessly with your existing infrastructure and aligns with your team’s expertise often provides better long-term value than a technically superior solution that requires extensive learning curves or custom integration work. The most sophisticated encoding technology provides limited benefit if your team struggles to implement and maintain it effectively.
The IPTV landscape continues evolving rapidly, with new protocols, codecs, and delivery mechanisms regularly emerging. While you can’t predict all future developments, choosing encoders from vendors with strong development track records and clear upgrade paths helps protect your investment as the technology landscape evolves. IPTV encoder encoders.

Your encoder selection represents a foundational decision that will impact your streaming operations for years to come. Taking the time to thoroughly evaluate your options using the framework provided in this guide helps ensure that your choice supports both your current success and future growth. The investment in careful encoder selection pays dividends through improved reliability, better viewer experiences, and reduced operational overhead throughout the encoder’s service life. IPTV encoder encoders.
Need help configuring your IPTV encoder setup guide once you’ve made your selection? Our comprehensive configuration tutorials and troubleshooting resources can help you optimize your encoding infrastructure for maximum performance and reliability. IPTV encoder encoders.





