Introduction
Are your IPTV streams optimized for 4K efficiency and minimal buffering? With over 4.8 billion global internet users consuming video content daily, the demand for high-quality, bandwidth-efficient streaming has never been higher. Modern HEVC IPTV encoder technology addresses critical pain points that have plagued broadcasters for years: excessive bandwidth consumption, latency issues, and compromised video quality during peak traffic periods.
The streaming landscape has evolved dramatically, with IPTV market growth projected to reach $194.21 billion by 2025. Live streaming demand has surged by 99% since 2019, pushing content creators, IPTV resellers, and broadcasters to seek more efficient encoding solutions. Traditional H.264 codecs, while reliable, consume significantly more bandwidth compared to their H.265 counterparts, making HEVC IPTV encoder systems essential for competitive streaming operations.
Whether you’re an IPTV business owner looking to reduce operational costs, a content creator scaling your live streaming setup, or a technical professional optimizing broadcast infrastructure, understanding HEVC encoder capabilities will directly impact your streaming success. This comprehensive guide explores seven transformative benefits of HEVC encoding technology, practical setup instructions, performance benchmarks, and real-world applications that demonstrate why upgrading to an HEVC IPTV encoder isn’t just recommended—it’s necessary for staying competitive in 2025’s streaming ecosystem.
What is an HEVC IPTV Encoder?
An HEVC IPTV encoder is a specialized device or software application that compresses video content using the High Efficiency Video Coding (H.265) standard, specifically designed for Internet Protocol Television delivery. Unlike traditional broadcast methods, IPTV requires digital video streams to be packaged, compressed, and transmitted over IP networks while maintaining optimal quality-to-bandwidth ratios.

Hardware vs Software Encoders
Hardware encoders are dedicated physical devices featuring specialized chips designed exclusively for video compression. These units excel in reliability, consistent low latency (typically 50-100ms), and can operate continuously without performance degradation. Professional broadcasters and IPTV service providers typically prefer hardware solutions for mission-critical applications where stream stability is paramount.
Software encoders, conversely, utilize computer processing power to perform encoding tasks. They offer superior flexibility, allowing real-time parameter adjustments, multiple codec support, and cost-effective scalability. Software-based HEVC IPTV encoder solutions work exceptionally well for content creators, small-scale IPTV operations, and environments requiring frequent configuration changes.
H.265 vs H.264 Efficiency
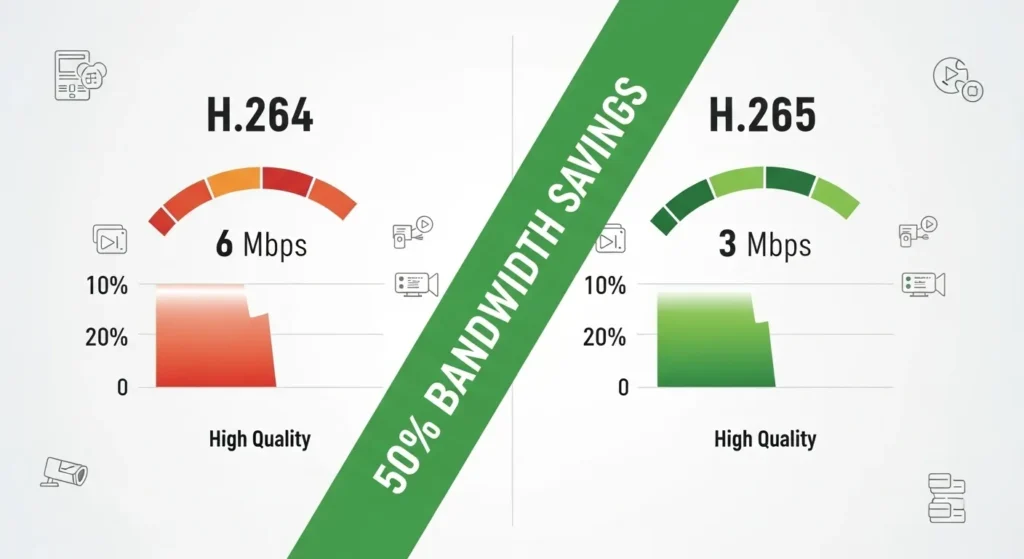
The transition from H.264 to H.265 represents a significant technological advancement in video compression. H.265 encoder technology delivers approximately 50% better compression efficiency compared to H.264, meaning identical video quality requires half the bandwidth. For a 1080p stream that previously required 6 Mbps using H.264, an HEVC IPTV encoder can achieve the same quality at just 3 Mbps, dramatically reducing bandwidth costs and improving viewer experience in limited connectivity scenarios.
This efficiency gain becomes even more pronounced with 4K content, where H.264 streams might consume 25-30 Mbps while H.265 delivers equivalent quality at 12-15 Mbps. For IPTV providers serving thousands of concurrent viewers, these bandwidth savings translate to substantial cost reductions and improved service reliability.
Top Benefits of HEVC IPTV Encoders
1. Exceptional Bandwidth Efficiency
HEVC IPTV encoder systems deliver unmatched compression efficiency, reducing bandwidth requirements by up to 50% compared to legacy H.264 solutions. This efficiency directly translates to lower Content Delivery Network (CDN) costs for IPTV providers and improved streaming performance for end-users with limited internet connections.
Consider a practical scenario: an IPTV service delivering 100 concurrent 1080p streams. Using H.264 encoding requires approximately 600 Mbps total bandwidth, while an H.265 encoder accomplishes the same delivery quality using just 300 Mbps. This reduction enables providers to serve double the audience using existing infrastructure or significantly reduce operational expenses.
2. Superior Video Quality Preservation
Advanced video compression algorithms in HEVC maintain exceptional visual fidelity even at lower bitrates. The codec’s improved motion estimation, better intra-prediction, and enhanced entropy coding preserve fine details, reduce blocking artifacts, and maintain color accuracy across various content types.
Sports broadcasts, which feature rapid motion and complex scenes, particularly benefit from HEVC encoding. Traditional codecs often struggle with fast-paced action, resulting in motion blur or pixelation. HEVC IPTV encoder technology handles these challenging scenarios while maintaining broadcast-quality output suitable for professional distribution.
3. Enhanced Multi-Device Compatibility
Modern IPTV hardware must support diverse viewing devices, from smartphones and tablets to smart TVs and set-top boxes. HEVC encoding ensures optimal playback across this device ecosystem while maintaining consistent quality standards. The codec’s scalability features allow single-source encoding with multiple output profiles, automatically adapting to different screen sizes and processing capabilities.

4. Advanced Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
Adaptive bitrate streaming represents a crucial feature for maintaining viewer satisfaction across varying network conditions. HEVC IPTV encoder systems can generate multiple quality tiers from a single source, automatically switching between bitrates based on real-time network performance. This technology prevents buffering interruptions while maximizing video quality within available bandwidth constraints.
5. Reduced Storage Requirements
For IPTV services offering Video-on-Demand (VOD) content, storage efficiency directly impacts operational costs. HEVC compression reduces file sizes by approximately 50% compared to H.264, enabling providers to store twice the content using existing infrastructure. This efficiency becomes particularly valuable for services maintaining extensive libraries of movies, series, and archived programming.
6. Lower Latency Performance
Hardware-based HEVC IPTV encoder solutions achieve glass-to-glass latency as low as 50 milliseconds, making them suitable for interactive applications, live sports betting, and real-time communication scenarios. This performance advantage ensures viewers receive content with minimal delay, crucial for time-sensitive programming and competitive streaming services.
7. Future-Proof Investment Protection
Investing in HEVC IPTV encoder technology provides long-term value as the industry transitions toward higher resolution content and immersive formats. The codec’s efficiency improvements ensure compatibility with emerging standards while maintaining backward compatibility with existing infrastructure and devices.
Types of HEVC IPTV Encoders
Hardware Encoders: Professional Reliability
Hardware-based HEVC IPTV encoder solutions offer unmatched reliability for professional broadcasting environments. These dedicated devices feature custom silicon optimized for H.265 compression, delivering consistent performance during extended operation periods. Key advantages include:
Reliability and Stability: Hardware encoders operate independently of computer systems, eliminating crashes, software conflicts, and performance inconsistencies associated with general-purpose computing platforms. Many professional units offer 99.9% uptime ratings suitable for 24/7 broadcast operations.
Optimized Performance: Dedicated encoding chips process video streams more efficiently than software solutions, resulting in lower power consumption, reduced heat generation, and superior encoding quality. This optimization enables single units to handle multiple simultaneous streams without performance degradation.
Professional Connectivity: Hardware IPTV hardware typically includes comprehensive input/output options, supporting HDMI, SDI, composite, and component connections. This versatility accommodates diverse source equipment without requiring additional converters or adapters.
Software Encoders: Flexible and Cost-Effective
Software-based HEVC IPTV encoder solutions provide exceptional flexibility for dynamic streaming environments. These applications leverage computer processing power to perform encoding tasks, offering several distinct advantages:
Cost Effectiveness: Software encoders eliminate dedicated hardware costs while providing professional encoding capabilities. This approach works particularly well for content creators, small IPTV operators, and organizations with budget constraints.
Upgradeable Technology: Software solutions receive regular updates introducing new features, codec improvements, and bug fixes. Users benefit from continuous enhancement without hardware replacement costs.
Customization Options: Software encoders often provide extensive configuration options, allowing fine-tuning of encoding parameters, custom overlays, and integration with third-party applications through APIs and plugins.
Key Features to Look For
Resolution and Framerate Support
Modern HEVC IPTV encoder systems should support resolutions from 480p through 4K (3840×2160) at various framerates including 24, 30, 50, and 60 fps. Professional applications may require 8K support, while most IPTV services focus on 1080p and 4K capabilities. Ensure your chosen encoder handles your target resolution with adequate processing headroom for future expansion.
Comprehensive Codec Support
While HEVC represents the primary encoding standard, versatile IPTV hardware should support multiple codecs including H.264 (AVC), H.265 (HEVC), VP9, and emerging AV1 standards. This flexibility ensures compatibility with diverse viewing devices and future-proofs your investment as codec standards evolve.
Streaming Protocol Compatibility
Professional HEVC IPTV encoder solutions must support industry-standard streaming protocols including:
- RTMP streaming for platforms like YouTube Live, Facebook Live, and Twitch
- RTSP for IP camera integration and surveillance applications
- HLS (HTTP Live Streaming) for adaptive bitrate delivery
- DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming) for cross-platform compatibility
- SRT (Secure Reliable Transport) for low-latency streaming over unpredictable networks
Network and Connectivity Options
Robust networking capabilities distinguish professional encoders from consumer-grade solutions. Look for Gigabit Ethernet ports, Wi-Fi connectivity, and multiple simultaneous stream outputs. Advanced units may include failover networking, bandwidth monitoring, and Quality of Service (QoS) prioritization features.
HDMI to IP conversion capabilities should support various input formats while maintaining signal integrity. Professional encoders often include loop-through outputs, allowing signal distribution to multiple destinations without quality loss.
Step-by-Step Setup Instructions
Step 1: Connect Your Source Input
Begin your HEVC IPTV encoder setup by establishing source connections. For HDMI to IP conversion, connect your video source (camera, computer, media player) to the encoder’s HDMI input using high-quality cables. Ensure cable length doesn’t exceed manufacturer recommendations to prevent signal degradation.
Pro Tip: For professional installations, use HDMI cables with built-in signal amplification for runs exceeding 25 feet. Always verify input signal format matches encoder capabilities before proceeding.
Step 2: Configure Network Settings
Access the encoder’s web interface through its default IP address (typically found in documentation or device label). Configure network parameters including:
- Static IP address within your network range
- Subnet mask and default gateway
- DNS server addresses for internet connectivity
- Network Time Protocol (NTP) for accurate timestamps
Advanced Configuration: Enable QoS settings to prioritize video traffic, configure VLANs for network segregation, and set up SNMP monitoring for professional environments.
Step 3: Set Stream Destination
Configure your HEVC IPTV encoder output destinations based on your streaming requirements:
For YouTube Live:
- Server URL: rtmp://a.rtmp.youtube.com/live2/
- Stream Key: (obtained from YouTube Live dashboard)
- Protocol: RTMP
For IPTV Servers:
- Destination IP and port
- Streaming protocol (HLS, DASH, or RTSP)
- Authentication credentials if required
For Multiple Destinations: Many encoders support simultaneous streaming to multiple platforms, allowing broader audience reach without additional hardware.
Step 4: Optimize Bitrate and Resolution
Configure encoding parameters based on your target audience and network capabilities:
For 1080p Streaming:
- Resolution: 1920×1080
- Bitrate: 3-6 Mbps (H.265)
- Keyframe interval: 2 seconds
- Profile: Main or High
For 4K Streaming:
- Resolution: 3840×2160
- Bitrate: 12-20 Mbps (H.265)
- Keyframe interval: 2 seconds
- Profile: Main 10-bit for HDR content
Step 5: Go Live and Monitor Performance
Initiate your stream and monitor key performance indicators:
- Encoding bitrate stability
- Network utilization
- Stream health indicators
- Viewer connectivity metrics
Pro Tips for Smooth Setup:
- Always test streams with low viewer counts before major broadcasts
- Configure automatic restart functions for 24/7 operations
- Set up email alerts for stream interruptions or hardware failures
- Maintain backup encoding paths for critical broadcasts
- Document configuration settings for rapid deployment replication
Performance Benchmarks & Comparisons
Hardware Encoder Performance Metrics
Professional hardware-based HEVC IPTV encoder solutions typically deliver superior performance compared to software alternatives. Industry-standard hardware encoders achieve:
Maximum Resolution: Up to 4K (3840×2160) at 60 fps with some premium units supporting 8K encoding Bitrate Range: 100 Kbps to 50+ Mbps depending on model and configuration Latency Performance: 50-100ms glass-to-glass delay under optimal conditions Simultaneous Streams: 1-16 concurrent outputs depending on resolution and bitrate settings

Software Encoder Capabilities
Software-based H.265 encoder solutions leverage computer processing power, resulting in variable performance based on system specifications:
CPU Requirements: Intel i7 or AMD Ryzen 7 minimum for 4K encoding RAM Usage: 8-16 GB recommended for stable operation Maximum Resolution: Limited by system capabilities, typically 4K at 30 fps Latency Performance: 100-300ms depending on encoding complexity and system load
Comparative Analysis: Hardware vs Software
| Feature | Hardware Encoder | Software Encoder |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | $2,000-$15,000 | $100-$500 |
| Operating Cost | Low power consumption | Higher electricity usage |
| Reliability | 99.9% uptime | Variable, system dependent |
| Latency | 50-100ms | 100-300ms |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Regular updates required |
| Scalability | Fixed capacity | Flexible, upgrade dependent |
Real-World Performance Scenarios
Scenario 1: Corporate Live Streaming A medium-sized company streaming weekly all-hands meetings requires consistent 1080p quality for 500+ employees. A hardware HEVC IPTV encoder delivers stable performance with 3 Mbps bitrate, ensuring reliable delivery across corporate networks while maintaining professional presentation quality.
Scenario 2: IPTV Service Provider An IPTV reseller managing 50 concurrent channels benefits from hardware encoder efficiency. Using H.265 compression, the provider reduces bandwidth costs by 40% compared to previous H.264 infrastructure while supporting additional channel capacity for business growth.
Scenario 3: Educational Institution A university’s distance learning program utilizes software HEVC IPTV encoder solutions for lecture capture and live streaming. The flexible configuration accommodates various classroom setups while keeping costs manageable for budget-conscious educational environments.
Use Cases for IPTV Resellers and Broadcasters
Live Channel Distribution and VOD Services
IPTV resellers leverage HEVC IPTV encoder technology to deliver professional channel lineups while minimizing bandwidth expenses. The improved compression efficiency enables smaller operators to compete with established providers by offering more channels within limited infrastructure budgets.
Live Broadcasting Benefits: Real-time encoding supports breaking news, sports events, and live entertainment programming. Advanced video compression maintains broadcast quality while accommodating network fluctuations and varying viewer demands.
VOD Optimization: Pre-encoded HEVC content reduces storage requirements and improves server response times. Libraries containing thousands of movies and series benefit from 50% storage savings compared to legacy H.264 encoding.

Corporate and Educational Streaming
Organizations increasingly rely on live video broadcasting for internal communications, training programs, and public outreach initiatives. HEVC IPTV encoder systems support these applications through:
Corporate Communications: Executive presentations, town halls, and training sessions reach distributed workforces efficiently. Low-latency encoding enables interactive Q&A sessions and real-time feedback.
Educational Applications: Distance learning platforms utilize adaptive bitrate streaming to accommodate students with varying internet connectivity. Recorded lectures maintain exceptional quality while minimizing storage and bandwidth costs.
OTT Platform Development and Special Events
Over-the-top (OTT) platform developers require scalable encoding solutions supporting rapid audience growth. IPTV hardware provides the reliability and performance necessary for professional streaming services competing with established platforms.
Event Broadcasting: Conferences, concerts, and sporting events benefit from HEVC’s efficiency when serving large concurrent audiences. The technology enables high-quality streams without overwhelming network infrastructure during peak viewing periods.
Multi-Platform Distribution: Single-source encoding with multiple output formats streamlines content distribution across websites, mobile apps, and connected TV platforms. This efficiency reduces operational complexity while maintaining consistent quality standards.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Incorrect Streaming Protocol Selection
Many users overlook streaming protocol compatibility when configuring their HEVC IPTV encoder systems. Using RTMP for applications requiring ultra-low latency or selecting HLS for real-time interactive streaming can significantly impact performance.
Solution: Match protocols to specific use cases. Use RTMP streaming for established platforms, SRT for low-latency applications, and HLS/DASH for adaptive bitrate delivery to diverse viewing devices.
Neglecting Firmware Updates
Outdated firmware often contains security vulnerabilities and performance limitations that impact streaming quality and reliability. Many users install encoders without establishing update schedules, leading to compatibility issues and missed feature enhancements.
Prevention Strategy: Schedule monthly firmware checks and implement update procedures during maintenance windows. Subscribe to manufacturer newsletters for update notifications and security bulletins.
Overloading Bitrate Settings
Inexperienced users frequently configure excessive bitrates, believing higher numbers guarantee better quality. This approach wastes bandwidth, increases buffering likelihood, and may exceed network capacity during peak usage periods.
Optimal Configuration: Start with manufacturer recommendations then adjust based on actual performance metrics. Monitor viewer connection statistics to identify optimal bitrate ranges for your audience demographics.
Inadequate Network Planning
Insufficient network capacity planning causes stream interruptions, quality degradation, and viewer frustration. Many installations underestimate total bandwidth requirements when supporting multiple concurrent streams.
Solution: Calculate total bandwidth requirements including safety margins for peak usage. Implement QoS policies prioritizing video traffic and configure failover connections for critical applications.
Ignoring Environmental Factors
Hardware IPTV hardware requires proper ventilation and environmental controls for optimal performance. Poor airflow, excessive temperatures, and dusty environments cause premature failure and performance degradation.
Prevention Measures: Maintain ambient temperatures below 75°F (24°C), ensure adequate airflow around devices, and implement regular cleaning schedules for air intake filters.
Maintenance & Longevity Tips
Regular Hardware Maintenance
Professional HEVC IPTV encoder systems require systematic maintenance for optimal longevity and performance. Establish monthly inspection schedules addressing:
Airflow and Cooling: Clean intake vents and exhaust ports to prevent dust accumulation. Verify cooling fan operation and replace filters according to manufacturer specifications. Monitor internal temperatures through management interfaces and adjust environmental controls as needed.
Connection Integrity: Inspect all cable connections for corrosion, wear, or loosening. HDMI and network cables should be secured properly to prevent intermittent connectivity issues. Replace cables showing signs of damage before they cause stream interruptions.
Software and Firmware Management
Maintain current software versions to ensure optimal security, compatibility, and feature access:
Update Scheduling: Implement systematic update procedures during planned maintenance windows. Test new firmware versions in non-production environments before deploying to critical systems.
Configuration Backup: Regularly backup encoder configurations to enable rapid recovery after hardware failures or configuration errors. Store backups both locally and in secure off-site locations.
Security Hardening: Change default passwords, disable unnecessary services, and implement network access controls. Regular security audits help identify potential vulnerabilities before they impact operations.
Performance Monitoring and Optimization
Establish monitoring systems tracking key performance indicators:
Stream Health Metrics: Monitor bitrate stability, frame drops, and encoding errors through management interfaces or third-party monitoring tools. Set up automated alerts for threshold violations.
Network Performance: Track bandwidth utilization, packet loss, and latency metrics. Identify trends indicating network capacity limitations or connectivity issues requiring attention.
Resource Utilization: Monitor CPU, memory, and storage utilization for software encoders. Plan hardware upgrades before resource constraints impact streaming quality.
Preventive Replacement Strategies
Develop replacement schedules for components with limited lifespans:
Cooling Fans: Replace cooling fans every 2-3 years in continuous operation environments. Keep spare fans in inventory for immediate replacement.
Storage Devices: SSDs and hard drives have finite lifespans. Monitor drive health indicators and replace drives showing early warning signs.
Backup Systems: Maintain spare encoders for critical applications. Hot-standby configurations enable rapid failover during primary system failures.
Conclusion & Recommendations
The evolution of streaming technology has made HEVC IPTV encoder systems essential infrastructure for competitive content delivery in 2025. The seven transformative benefits explored throughout this guide—bandwidth efficiency, superior quality preservation, multi-device compatibility, adaptive streaming capabilities, reduced storage requirements, low-latency performance, and future-proof investment protection—demonstrate why upgrading from legacy H.264 systems represents both operational necessity and strategic advantage.
For IPTV service providers, the 50% bandwidth reduction achieved through H.265 encoder technology directly translates to substantial cost savings and improved service reliability. Content creators benefit from enhanced streaming quality and broader platform compatibility, while enterprises gain professional broadcasting capabilities supporting modern communication requirements.
The choice between hardware and software HEVC IPTV encoder solutions depends on specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and scalability needs. Hardware encoders excel in mission-critical applications requiring maximum reliability and consistent low latency, while software solutions provide flexibility and cost-effectiveness for dynamic streaming environments.
Success with HEVC IPTV encoder implementation requires careful attention to setup procedures, ongoing maintenance practices, and performance optimization strategies. Avoiding common configuration mistakes and implementing systematic monitoring ensures long-term operational success and viewer satisfaction.
The streaming industry’s continued evolution toward higher resolutions, immersive formats, and interactive experiences makes HEVC encoding technology a foundational investment for future growth. Organizations implementing HEVC IPTV encoder systems today position themselves advantageously for emerging opportunities in live streaming, OTT platforms, and next-generation content delivery services.
Upgrade your IPTV broadcast today with an HEVC IPTV encoder. Share your setup experiences or subscribe to our newsletter for more advanced streaming tutorials and industry insights!

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What’s the difference between an encoder and a transcoder?
An HEVC IPTV encoder converts raw video signals into compressed digital streams suitable for transmission over IP networks. The device takes uncompressed video inputs (HDMI, SDI) and creates encoded streams using H.265 compression algorithms.
A transcoder, conversely, converts existing encoded video from one format to another. For example, transcoding might convert an H.264 stream to H.265 format or change resolution from 4K to 1080p. Transcoders work with already-compressed video content rather than raw signals.
Many modern IPTV hardware devices combine both functions, accepting raw video inputs for encoding while simultaneously transcoding existing streams for multi-format distribution.
Q2: Can one HEVC IPTV encoder stream to multiple platforms simultaneously?
Yes, most professional HEVC IPTV encoder systems support simultaneous streaming to multiple destinations. This capability, called “multi-streaming” or “simulcasting,” allows broadcasters to reach audiences across different platforms without requiring multiple encoding devices.
Common simultaneous streaming scenarios include:
- RTMP streaming to YouTube Live, Facebook Live, and Twitch concurrently
- Delivering different quality tiers to various streaming protocols (HLS, DASH, RTSP)
- Broadcasting to both public platforms and private IPTV servers
The number of simultaneous streams depends on encoder processing power, network bandwidth, and configured bitrate settings. Hardware encoders typically support 2-8 concurrent streams, while software solutions scale based on computer specifications.
Q3: Do HEVC IPTV encoders support 4K resolution streaming?
Modern HEVC IPTV encoder systems fully support 4K (3840×2160) streaming with frame rates up to 60 fps. The H.265 codec’s efficiency makes 4K streaming practical over standard internet connections, requiring approximately 12-20 Mbps compared to 25-40 Mbps needed for equivalent H.264 quality.
Professional hardware encoders typically include dedicated 4K processing capabilities, ensuring stable performance during extended broadcasts. Software encoders can handle 4K encoding but require powerful computer systems with sufficient CPU and RAM resources.
4K Streaming Considerations:
- Ensure adequate upload bandwidth (minimum 25 Mbps recommended)
- Verify target platforms support 4K HEVC delivery
- Monitor viewer device compatibility for optimal playback experience
- Consider adaptive bitrate streaming for audiences with varying connection speeds
Advanced IPTV hardware may also support emerging 8K formats, though widespread adoption remains limited due to bandwidth and device compatibility constraints.





