Introduction: Why Encoder IPTV Matters in 2025
An Encoder IPTV is the backbone of any high-quality streaming setup, transforming raw video signals into compressed, broadcast-ready streams that deliver exceptional viewer experiences across multiple devices and networks. In 2025’s competitive streaming landscape, choosing the right encoder IPTV solution can make the difference between seamless content delivery and frustrated viewers abandoning your stream.

The modern streaming ecosystem demands more than basic video compression. Today’s IPTV providers, broadcasters, and content creators need encoders that deliver ultra-low latency streaming, support multiple output protocols simultaneously, and maintain consistent quality even during network fluctuations. Whether you’re running a small-scale IPTV service or managing enterprise-level broadcast operations, your choice directly impacts uptime, viewer satisfaction, and ultimately, your bottom line.
Recent industry data shows that 78% of viewers will abandon a stream within 10 seconds if they encounter buffering or quality issues. This statistic underscores why investing in proper encoder IPTV infrastructure isn’t just a technical decision—it’s a business-critical investment that affects customer retention and revenue growth.
Table of Contents
How Encoder IPTV Works: A Simplified Overview
Understanding encoder IPTV fundamentals helps you make informed purchasing decisions. At its core, It device captures raw video signals from cameras, satellite feeds, or other sources, then compresses this data using advanced codecs like H.264, H.265/HEVC, or the newer AV1 standard.
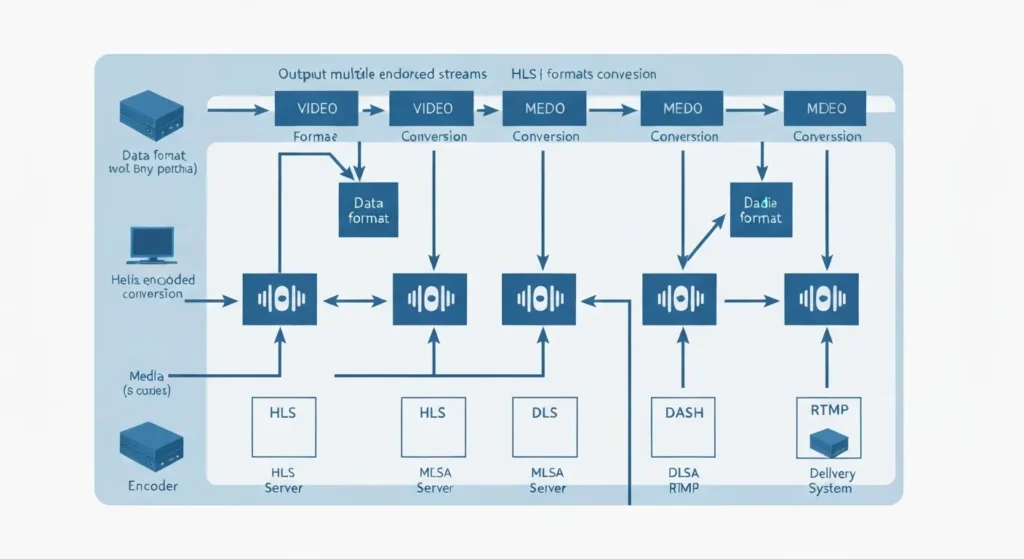
The encoding process involves several critical steps:
Video Signal Capture: The encoder receives uncompressed video data through various input interfaces including SDI, HDMI, IP streams, or analog connections. Professional-grade encoder IPTV units typically support multiple simultaneous inputs for redundancy and multi-camera setups.
Real-Time Compression: Advanced algorithms compress the video data while preserving quality. Modern encoders use hardware acceleration (dedicated chips) or software processing (CPU/GPU) to handle this computationally intensive task. The choice between hardware and software encoding affects latency, quality, and system resource requirements.
Multi-Protocol Output: Today’s encoder IPTV solutions generate multiple output streams simultaneously. A single encoder might output RTMP for social media platforms, HLS for mobile devices, SRT for reliable transmission over unreliable networks, and RTSP for direct streaming applications.
Adaptive Streaming: Professional encoder IPTV systems create multiple bitrate versions of the same content, allowing viewers’ devices to automatically switch between quality levels based on their internet connection speed and device capabilities.
The key difference between real-time encoding (live streams) and pre-recorded content lies in processing constraints. Live encoding must maintain strict timing requirements—any delay longer than your target latency threshold will degrade the viewing experience or make interactive applications impossible.
Hardware IPTV Encoders: Benefits and Limitations
Hardware encoder IPTV solutions use dedicated processing chips specifically designed for video compression tasks. These purpose-built devices offer several distinct advantages that make them preferred choices for mission-critical streaming applications.
Performance Consistency: Hardware encoders deliver predictable, stable performance regardless of system load. Unlike software solutions that compete for CPU resources with other applications, dedicated encoder IPTV hardware maintains consistent throughput and latency even during peak processing demands.
Lower Latency: Hardware-based encoding typically achieves sub-second latency, crucial for live sports broadcasting, interactive streaming, and real-time communication applications. Professional hardware encoder IPTV units can deliver glass-to-glass latency as low as 200-500 milliseconds.
Reliability and Uptime: Purpose-built encoder IPTV hardware often includes redundant power supplies, failover mechanisms, and robust cooling systems. These features are essential for broadcast environments where downtime costs thousands of dollars per minute.
Energy Efficiency: Dedicated encoding chips consume significantly less power than general-purpose processors handling the same workload. This efficiency translates to lower operating costs and reduced cooling requirements in server rack environments.
However, hardware encoder IPTV solutions also present certain limitations. Initial costs are typically higher than software alternatives, especially for professional-grade units supporting multiple simultaneous streams. Hardware encoders also offer less flexibility for rapid deployment changes or feature updates, as modifications often require firmware updates or physical hardware changes rather than simple software configuration adjustments.
Software IPTV Encoders: Flexibility vs. Resource Demands
Software encoder IPTV solutions run on standard computer hardware, using CPU and GPU resources to perform video compression tasks. This approach offers compelling advantages for many streaming applications, particularly those requiring frequent configuration changes or rapid scaling.

Deployment Flexibility: Software encoders can be installed on existing server infrastructure, virtual machines, or cloud computing platforms. This flexibility allows operators to leverage existing IT investments and quickly adapt to changing capacity requirements without purchasing dedicated hardware.
Feature Richness: Software encoder IPTV platforms often include advanced features like real-time video processing, graphics overlay capabilities, multi-camera switching, and integration with content management systems. These features are typically more expensive or unavailable in hardware-only solutions.
Scalability: Cloud-based software encoder IPTV deployments can automatically scale processing capacity based on demand. During high-traffic events, additional virtual encoder instances can be spawned automatically, then shut down when demand decreases to optimize costs.
Update Frequency: Software encoders receive frequent updates adding new features, codec support, and protocol compatibility. This ongoing development ensures your encoder IPTV solution stays current with evolving industry standards.
The primary challenge with software encoder IPTV solutions lies in resource management. High-quality encoding is computationally intensive, requiring substantial CPU or GPU resources. A single 4K encoder might consume 60-80% of a modern server’s processing capacity, necessitating careful resource planning and potentially dedicated hardware despite using software solutions.
Key Features to Look For in a Modern Encoder IPTV
Selecting the optimal it solution requires evaluating features that directly impact your streaming quality, operational efficiency, and future scalability needs. Modern encoders must support diverse protocols, deliver consistent performance, and integrate seamlessly with existing infrastructure.

Multi-Protocol Support: Today’s encoder IPTV must output multiple streaming protocols simultaneously. Essential protocols include SRT (Secure Reliable Transport) for transmission over unreliable networks, RTMP for social media platform integration, HLS (HTTP Live Streaming) for mobile device compatibility, and RTSP for direct streaming applications. Advanced units also support emerging protocols like WebRTC for ultra-low latency interactive streaming.
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming: Professional encoder IPTV solutions automatically generate multiple quality levels from a single input source. This capability allows viewers with different internet connection speeds and device capabilities to receive appropriately optimized streams without manual intervention.
Latency Optimization: Look for encoder IPTV units offering configurable latency modes. Ultra-low latency modes (under 1 second) are essential for interactive applications, while standard latency modes (2-5 seconds) may be acceptable for traditional broadcast content if they provide better quality or reliability.
Remote Management: Enterprise-grade encoder IPTV solutions include web-based management interfaces, SNMP monitoring support, and API integration capabilities. These features enable centralized monitoring of multiple encoders, automated configuration management, and integration with existing network operations center (NOC) systems.
Redundancy and Failover: Professional encoder IPTV units should support input redundancy (automatic switching between primary and backup video sources) and output redundancy (simultaneous streaming to multiple destinations). These features minimize service disruptions during equipment failures or network issues.
7 Powerful Tips to Optimize Your Encoder IPTV
Tip 1: Choose the Right Encoder Type for Your Workflow
The decision between hardware and software encoder IPTV solutions should align with your operational priorities and technical requirements. Hardware encoders excel in environments demanding consistent performance, minimal latency, and maximum reliability. Choose hardware solutions for:
- Live sports broadcasting requiring sub-second latency
- 24/7 streaming services where downtime is costly
- Remote locations with limited technical support
- Applications requiring multiple simultaneous high-quality outputs

Software encoder IPTV solutions work best when flexibility, feature richness, and cost efficiency are priorities. Consider software encoders for:
- Content creators needing frequent configuration changes
- Organizations with existing server infrastructure
- Cloud-based streaming services requiring elastic scaling
- Applications requiring advanced video processing features
Tip 2: Verify Protocol and Format Compatibility
Before purchasing any encoder IPTV solution, create a comprehensive compatibility matrix listing all required input sources, output destinations, and intermediate systems. Common compatibility issues include:
Input Format Support: Ensure your encoder supports all required input formats including resolution, frame rates, and color spaces. Professional encoders should handle 4K sources at 60fps, HDR content, and various aspect ratios without quality degradation.
Output Protocol Requirements: Map each streaming destination to its required protocol and configuration. YouTube requires RTMP with specific keyframe intervals, while enterprise IPTV systems might need SRT with custom encryption parameters.
Codec Compatibility: Verify that your encoder IPTV supports codecs required by your target devices and networks. H.265/HEVC provides better compression than H.264 but requires more processing power and isn’t universally supported by older devices.
Tip 3: Test Latency in Real-World Conditions
Latency specifications from encoder IPTV manufacturers often represent best-case laboratory conditions rather than real-world performance. Conduct thorough testing using your actual network infrastructure, streaming destinations, and typical network conditions.

End-to-End Measurement: Measure complete glass-to-glass latency from video source input to viewer display output. This comprehensive measurement reveals cumulative delays from encoding, network transmission, buffering, and decoding processes.
Network Condition Simulation: Test encoder IPTV performance under various network conditions including packet loss, jitter, and bandwidth limitations. Many encoders perform well under ideal conditions but struggle when networks become congested or unreliable.
Load Testing: Evaluate encoder performance when generating multiple simultaneous outputs or processing multiple input sources. Some encoder IPTV units maintain low latency with single streams but experience significant delays when handling multiple concurrent streams.
Tip 4: Ensure Proper Cooling and Environmental Controls
It’s equipment generates substantial heat, particularly hardware units with dedicated processing chips running continuously at full capacity. Inadequate cooling leads to thermal throttling, reduced performance, and premature equipment failure.

Rack Ventilation: Install encoder IPTV units in properly ventilated server racks with adequate front-to-back airflow. Maintain recommended spacing between units and ensure hot exhaust air doesn’t recirculate to intake vents.
Environmental Monitoring: Deploy temperature monitoring systems that alert operators when rack temperatures exceed safe operating ranges. Some advanced encoder IPTV units include built-in temperature sensors and thermal protection systems.
Redundant Cooling: For critical applications, implement redundant cooling systems including backup fans or even redundant air conditioning systems. The cost of redundant cooling is minimal compared to revenue loss from encoder failures during important broadcasts.
Tip 5: Evaluate Integration with Existing Infrastructure
Your encoder IPTV solution must integrate seamlessly with existing video routing, monitoring, and management systems. Integration complexity often determines deployment timeline and ongoing operational efficiency.
Control System Integration: Modern encoder IPTV units should support standard control protocols including SNMP for network monitoring, REST APIs for automation, and serial control for integration with broadcast automation systems.
Workflow Compatibility: Ensure your chosen encoder fits existing production workflows without requiring extensive retraining or process changes. Consider factors like configuration backup/restore procedures, firmware update processes, and troubleshooting accessibility.
Monitoring Integration: Professional encoder IPTV solutions should provide detailed performance metrics including input signal status, encoding statistics, network utilization, and output stream health. These metrics must integrate with existing monitoring systems for centralized oversight.
Tip 6: Consider Total Cost of Ownership
Initial encoder IPTV purchase price represents only a fraction of long-term ownership costs. Comprehensive cost analysis should include ongoing operational expenses, support requirements, and upgrade paths.
Power Consumption: Calculate annual electricity costs for encoder IPTV operation. Hardware encoders typically consume 50-200 watts continuously, while software encoders running on server hardware might consume 300-500 watts or more depending on processing requirements.
Support and Maintenance: Factor in annual support costs, firmware update procedures, and potential hardware replacement schedules. Some encoder IPTV manufacturers include comprehensive support in purchase price, while others charge separately for technical support and software updates.
Scalability Costs: Evaluate costs for adding capacity as your streaming requirements grow. Hardware solutions typically require purchasing additional units, while software solutions might only need additional server resources or cloud computing capacity.
Tip 7: Regular Maintenance and Firmware Updates
Maintaining optimal encoder IPTV performance requires proactive maintenance procedures and staying current with firmware updates. Neglecting maintenance leads to performance degradation, security vulnerabilities, and unexpected failures.
Update Management: Develop systematic procedures for testing and deploying firmware updates. Test updates in non-production environments before applying to live streaming encoders, and maintain rollback procedures in case updates cause compatibility issues.
Performance Monitoring: Implement continuous monitoring of encoder IPTV performance metrics including CPU utilization, memory usage, network throughput, and output stream quality. Trending these metrics over time reveals gradual performance degradation before it affects stream quality.
Preventive Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance procedures including cleaning air filters, checking cooling system operation, verifying input/output connections, and reviewing configuration backup procedures.
Common Encoder IPTV Mistakes to Avoid
Learning from others’ mistakes can save significant time, money, and frustration when implementing encoder IPTV solutions. These common pitfalls affect organizations ranging from small content creators to major broadcast networks.

Overpaying for Unused Features: Many encoder IPTV buyers purchase feature-rich units far exceeding their actual requirements. A content creator streaming to a single platform doesn’t need enterprise-grade redundancy features, while a broadcaster might not need advanced graphics overlay capabilities. Carefully analyze your requirements before investing in premium features you’ll never use.
Ignoring Compatibility Issues: Assuming all encoder IPTV solutions work with all streaming platforms leads to expensive compatibility problems discovered during deployment. Different platforms have specific requirements for keyframe intervals, audio codecs, resolution restrictions, and protocol implementations. Verify compatibility with all intended destinations before purchase.
Inadequate Testing: Many organizations test encoder IPTV solutions under ideal conditions but fail to evaluate performance under real-world stress. Network congestion, input signal variations, and sustained operation over days or weeks reveal issues not apparent during brief testing periods.
Neglecting Network Infrastructure: Encoder IPTV performance depends heavily on network infrastructure quality. Organizations often upgrade encoders while neglecting network switches, internet connections, or internal network capacity. The most expensive encoder cannot overcome network bottlenecks or reliability issues.
Poor Documentation and Training: Implementing encoder IPTV solutions without proper documentation and operator training leads to configuration errors, suboptimal performance, and extended troubleshooting times. Invest time in creating operational procedures and training staff before deploying encoders in production environments.
Recommended Encoder IPTV Models for 2025
Selecting specific encoder IPTV models depends on your budget, performance requirements, and operational constraints. These recommendations cover various price ranges and application scenarios based on current market offerings and performance analysis.
Budget-Friendly Solutions ($200-$800)
Entry-Level Hardware Encoders: Basic hardware encoder IPTV units in this price range typically support single input sources with HDMI or SDI connectivity, output to multiple protocols simultaneously, and provide web-based configuration interfaces. These encoders work well for small-scale streaming operations, house of worship broadcasts, and educational institutions with limited budgets.
Software Encoder Packages: Comprehensive software encoder IPTV solutions running on existing hardware can provide excellent value for organizations with suitable server infrastructure. These packages often include advanced features like multi-camera switching, graphics overlay, and cloud integration capabilities.
Consider budget encoders for applications where advanced features aren’t critical, technical support requirements are minimal, and operational environments are controlled. Budget encoder IPTV solutions typically lack redundancy features and advanced monitoring capabilities essential for mission-critical applications.
Mid-Range Professional Options ($800-$3,000)
Professional Hardware Encoders: Mid-range encoder IPTV hardware provides excellent balance between features, performance, and cost. Units in this category typically support multiple input sources, advanced codec options including H.265/HEVC, comprehensive protocol support, and professional monitoring capabilities.
Enterprise Software Solutions: Professional software encoder IPTV packages designed for enterprise deployment include advanced management features, cluster operation capabilities, API integration, and comprehensive technical support. These solutions often provide better long-term value than hardware alternatives for organizations requiring frequent configuration changes or rapid scaling.
Mid-range encoder IPTV solutions work well for regional broadcasters, medium-sized content creators, corporate communications departments, and IPTV service providers serving hundreds to thousands of viewers simultaneously.
High-End Enterprise Solutions ($3,000+)
Enterprise Hardware Encoders: Premium encoder IPTV hardware includes redundant components, advanced cooling systems, extensive input/output connectivity, and sophisticated monitoring capabilities. These units often support dozens of simultaneous outputs, advanced video processing features, and integration with broadcast automation systems.
Carrier-Grade Software Platforms: Enterprise software encoder IPTV solutions provide massive scalability, geographic distribution capabilities, advanced analytics, and comprehensive service level agreement (SLA) support. These platforms can handle thousands of simultaneous streams across multiple data centers.
Enterprise encoder IPTV solutions are essential for major broadcasters, telecommunications companies, large-scale IPTV providers, and organizations where streaming reliability directly impacts revenue or safety.
Conclusion: Make a Smart, Future-Proof Encoder IPTV Choice
Selecting the optimal encoder IPTV solution requires balancing current requirements against future needs while considering budget constraints and operational capabilities. The seven powerful tips outlined in this guide provide a framework for making informed decisions that deliver long-term value and operational success.
Remember that encoder IPTV setup quality matters more than price alone. A properly configured mid-range encoder often outperforms an expensive unit deployed without adequate planning, testing, or infrastructure support. Focus on understanding your specific requirements, conducting thorough compatibility testing, and implementing proper operational procedures.

The streaming industry continues evolving rapidly, with new protocols, codecs, and viewer expectations emerging regularly. Choose encoder IPTV solutions from manufacturers with strong development track records and commitment to ongoing innovation. This approach ensures your investment remains relevant as technology advances and requirements change.
Success with encoder IPTV deployment depends on treating it as a system rather than an isolated component. Network infrastructure, monitoring systems, operational procedures, and staff training all contribute to overall streaming quality and reliability. By following these guidelines and avoiding common mistakes, you’ll be well-positioned to deliver exceptional streaming experiences that satisfy viewers and support your business objectives in 2025 and beyond.
The streaming landscape rewards organizations that prioritize quality, reliability, and viewer experience over simple cost minimization. Invest wisely in encoder IPTV infrastructure, implement proper operational procedures, and maintain focus on continuous improvement. Your viewers will notice the difference, and your business results will reflect their satisfaction.





