Introduction
Is your IPTV streaming setup delivering the stable, buffer-free quality your viewers expect in 2025? With global IPTV market revenues projected to reach $194.21 billion by 2025—a staggering 15.2% year-over-year growth—content providers face mounting pressure to deliver flawless streaming experiences. Yet, many broadcasters still struggle with persistent latency issues, compression artifacts, and unreliable streams that frustrate audiences and damage brand reputation.
The foundation of professional IPTV broadcasting lies in choosing the right IPTV encoder—the critical hardware that transforms raw video signals into streamable digital content. Whether you’re an IPTV reseller managing 24/7 channels, a church broadcasting services, or an esports venue streaming tournaments, your encoder determines everything from video quality to viewer retention rates.
Modern streaming demands have evolved beyond basic H.264 compression. Today’s audiences expect 4K resolution, ultra-low latency, and multi-platform distribution—all while maintaining rock-solid stability. The wrong encoder choice can mean the difference between seamless professional broadcasts and embarrassing stream failures during peak viewing moments.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dissect the five most powerful IPTV encoders dominating 2025, examine their technical specifications, and provide actionable setup strategies that guarantee superior streaming performance. From hardware specifications to real-world deployment scenarios, you’ll discover exactly which encoder matches your specific broadcasting needs.
Table of Contents
Core Components of an IPTV Encoder
Understanding IPTV hardware architecture is crucial before investing in any encoding solution. Professional IPTV encoders serve as digital translators, converting analog or digital video sources into compressed IP streams suitable for network transmission and playback across diverse devices. IPTV encoder.
Essential Input Interfaces:
- HDMI inputs for consumer devices and cameras
- SDI (Serial Digital Interface) for professional broadcasting equipment
- Composite and component video for legacy sources
- Audio embedding capabilities for synchronized sound
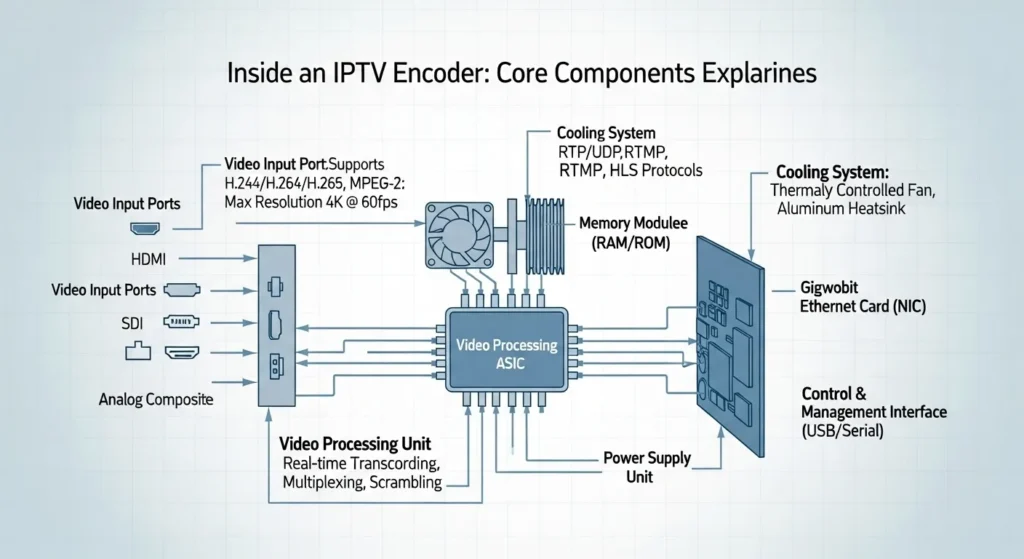
Codec Performance Standards: Modern encoders support multiple compression standards, with H.264 remaining the industry workhorse due to widespread device compatibility. However, H.265 (HEVC) encoders offer superior compression efficiency, reducing bandwidth requirements by up to 50% while maintaining equivalent video quality. Advanced units also support emerging codecs like AV1 for future-proofing investments.
Streaming Protocol Support: Professional-grade IPTV transcoder units must handle various streaming protocols seamlessly:
- RTMP (Real-Time Messaging Protocol) for platforms like YouTube Live and Facebook
- HLS (HTTP Live Streaming) for mobile and web delivery
- UDP multicast for IPTV distribution networks
- WebRTC for ultra-low latency applications
Beginner vs. Enterprise Distinction: Entry-level encoders typically offer plug-and-play simplicity with preset configurations, making them ideal for small venues and content creators. Enterprise solutions provide granular control over bitrate allocation, advanced error correction, and redundant streaming capabilities essential for mission-critical broadcasts. IPTV encoder.
Network integration capabilities separate professional units from consumer-grade alternatives. Look for encoders with dual Ethernet ports, VLAN support, and remote management interfaces that enable centralized control across multiple encoding locations. IPTV encoder.
Setup Time & Efficiency
Time-to-broadcast efficiency directly impacts operational costs and viewer satisfaction. Professional IPTV encoders should achieve stable streaming within 10-15 minutes of initial configuration, including network setup and destination platform integration.
Hardware vs. Software Encoder Comparison:
Hardware encoders excel in dedicated encoding scenarios, offering consistent performance without competing for system resources. These purpose-built devices typically feature:
- Dedicated ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) processors
- Consistent encoding performance regardless of system load
- Lower power consumption compared to PC-based solutions
- Reduced heat generation and improved reliability
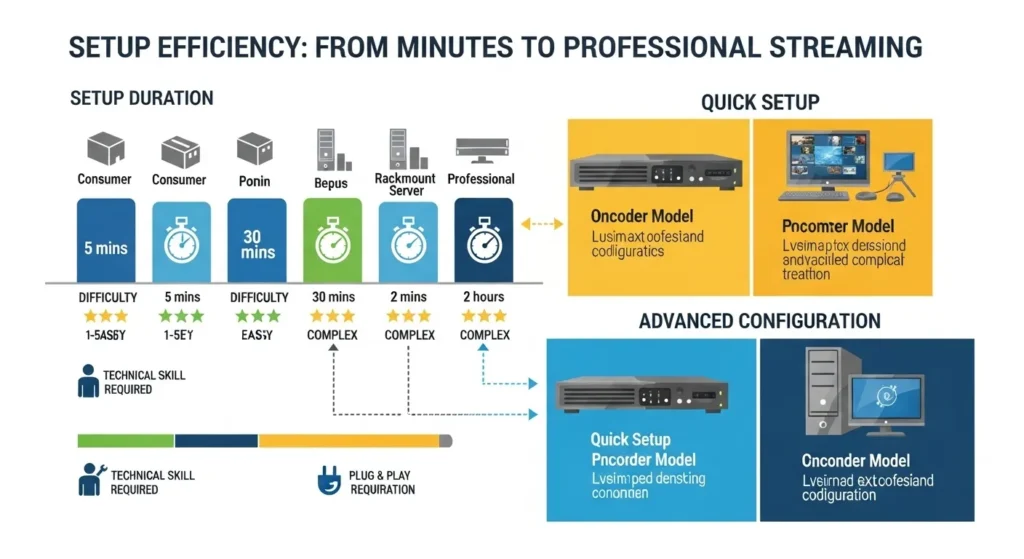
Software encoders provide flexibility and cost-effectiveness for multi-purpose streaming setups:
- Utilization of existing computer hardware
- Easy updates and feature additions
- Integration with existing production workflows
- Scalable processing based on available CPU/GPU resources
Network Configuration Speed Factors: Modern encoders support DHCP auto-configuration, eliminating manual IP assignment in most scenarios. However, professional deployments benefit from static IP addressing for consistent remote access and management. Quality units feature web-based configuration interfaces accessible via standard browsers, streamlining setup across different operating systems.
Optimization Timeline: Initial connection typically requires 2-3 minutes, while bitrate optimization and quality tuning add 5-8 minutes for optimal results. Experienced operators can reduce this to under 10 minutes with proper preparation and standardized configuration templates.
Step-by-Step Setup Instructions
Step 1: Connect Video Source
Begin by establishing your video input connection using the appropriate cable type for your source device. HDMI connections provide the simplest plug-and-play experience for most modern cameras and computers, while SDI inputs offer superior signal integrity for professional broadcasting equipment. IPTV encoder.
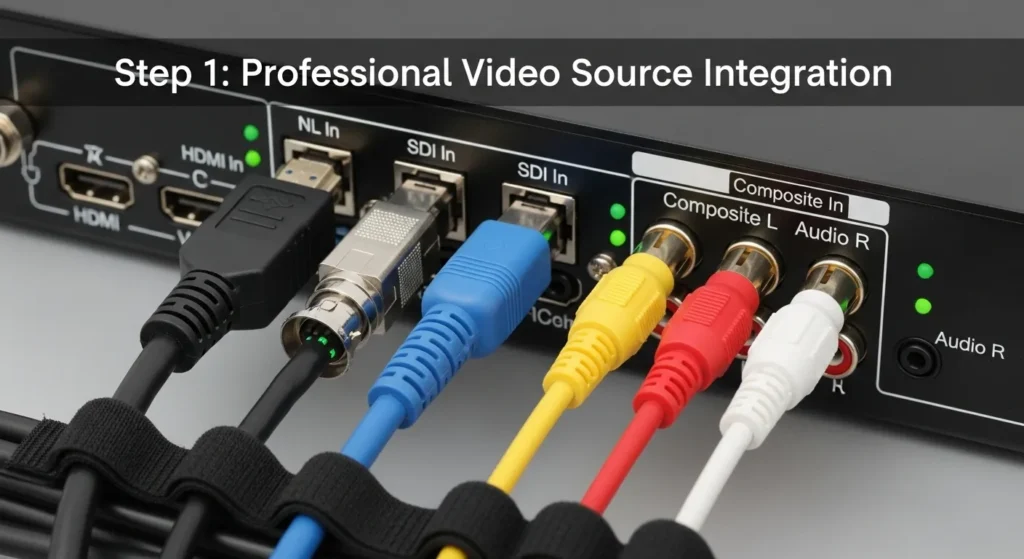

Verify input signal detection through the encoder’s status display or web interface. Most units automatically detect resolution and frame rate parameters, but manual configuration may be necessary for non-standard source formats.
Pro Tip: Always use high-quality cables rated for your maximum resolution requirements. Cheap HDMI cables can introduce signal dropouts that manifest as encoding glitches. IPTV encoder.
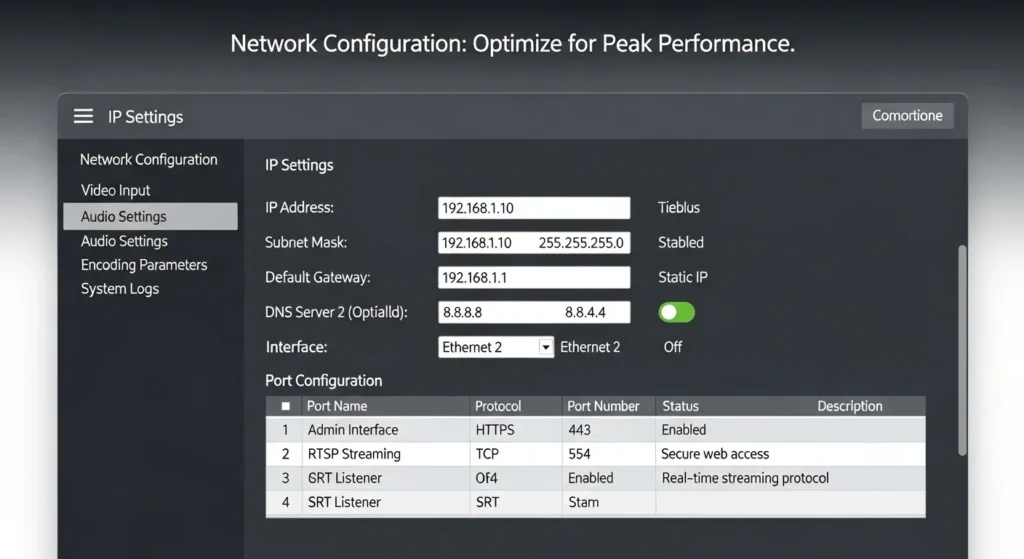
Step 2: Configure Network/IP Settings
Access the encoder’s network configuration through its web interface using the default IP address (typically found in the user manual or device label). Configure network parameters according to your infrastructure requirements:

- Assign static IP address within your network range
- Configure subnet mask and gateway settings
- Set DNS servers for reliable internet connectivity
- Enable NTP synchronization for accurate timestamping
Test network connectivity to ensure proper integration with your IPTV distribution infrastructure.
Step 3: Add Streaming Destinations
Configure your target streaming platforms by entering the appropriate server details:
For RTMP Destinations (YouTube, Facebook Live):
- Server URL provided by the streaming platform
- Stream key/password for authentication
- Backup server configuration for redundancy
For IPTV Server Integration:
- Multicast address and port configuration
- UDP streaming parameters
- Authentication credentials if required
Most professional encoders support simultaneous streaming to multiple destinations, enabling broader audience reach without additional hardware investment. IPTV encoder.
Step 4: Optimize Bitrate/Resolution Settings
Video quality optimization requires balancing visual fidelity against bandwidth constraints. Configure encoding parameters based on your specific application:
For 1080p Streaming:
- Video bitrate: 4-8 Mbps for high-quality content
- Audio bitrate: 128-256 kbps for stereo audio
- Keyframe interval: 2-4 seconds for optimal seeking
For 4K Applications:
- Video bitrate: 15-25 Mbps minimum
- Hardware acceleration essential for real-time performance
- Consider H.265 encoding for bandwidth efficiency
Step 5: Launch Stream
Initiate streaming after verifying all configuration parameters. Monitor the encoder’s status indicators and web interface for stream health information:
- Check encoder temperature and system load
- Verify network throughput meets bitrate requirements
- Monitor for dropped frames or encoding errors
- Confirm audio/video synchronization
Pro Tips for Reliability:
- Use wired Ethernet connections instead of Wi-Fi for critical applications
- Implement UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) backup for power protection
- Configure automatic stream restart in case of network interruptions
- Set up monitoring alerts for immediate notification of stream issues IPTV encoder.
Performance & Streaming Quality Benchmarks
Professional IPTV encoder performance directly correlates with viewer satisfaction and retention rates. Understanding key performance metrics enables informed equipment selection and optimal configuration for specific applications.
Resolution & Frame Rate Capabilities:
| Encoder Tier | Max Resolution | Frame Rates | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry Level | 1080p | 30/60fps | Small venues, basic streaming |
| Professional | 1080p/4K | 60/120fps | Sports, events, broadcast |
| Enterprise | 4K/8K | Variable | High-end production, future-proofing |
Bitrate Performance Ranges:
- Standard Definition (480p): 1-3 Mbps video, 64-128 kbps audio
- High Definition (1080p): 4-8 Mbps video, 128-256 kbps audio
- Ultra High Definition (4K): 15-40 Mbps video, 256-512 kbps audio
Latency Benchmarks: Low-latency streaming has become critical for interactive applications and live sports broadcasting:
- Standard RTMP: 3-10 seconds end-to-end latency
- Low-Latency RTMP: 1-3 seconds typical performance
- WebRTC Integration: Sub-second latency possible with proper configuration
Supported Streaming Protocols: Modern encoders must support multiple protocols for maximum compatibility:
- RTMP/RTMPS: Primary protocol for most streaming platforms
- HLS: Essential for mobile device compatibility
- MPEG-TS over UDP: Standard for IPTV distribution networks
- WebRTC: Emerging standard for ultra-low latency applications
- SRT (Secure Reliable Transport): Improving reliability over unstable networks
Compression Efficiency Metrics:
- H.264: Industry standard with broad compatibility
- H.265/HEVC: 40-50% better compression than H.264
- AV1: Next-generation codec with superior efficiency
- Hardware vs. Software: Dedicated chips offer consistent performance
Audio Processing Capabilities:
- Input Formats: Analog, digital, embedded audio support
- Encoding Standards: AAC, MP3, PCM options
- Channel Support: Stereo, 5.1, 7.1 surround sound
- Audio Sync: Automatic lip-sync correction features
Better Alternatives & Add-ons
Advanced IPTV hardware ecosystems extend beyond basic encoding to provide comprehensive streaming solutions tailored to specific industry requirements. IPTV encoder.
H.265 Encoder Advantages: Next-generation compression technology offers significant bandwidth savings without quality compromise. H.265 encoders particularly benefit:
- Bandwidth-Limited Environments: Reduce streaming costs by 40-50%
- Mobile Streaming: Improved quality on cellular connections
- Archive Storage: Dramatic reduction in storage requirements
- Multi-Stream Efficiency: More concurrent streams per network connection
Dual-Stream and Multi-Platform Devices: Professional broadcasters increasingly demand simultaneous streaming to multiple destinations:
- Primary/Backup Streams: Automatic failover for mission-critical applications
- Multi-Bitrate Streaming: Adaptive quality for diverse connection speeds
- Platform-Specific Optimization: Customized encoding for YouTube, Facebook, custom IPTV servers
- Geographic Distribution: Regional content delivery optimization
Audio Synchronization Modules: Professional productions require perfect audio/video alignment:
- Automatic Lip-Sync Correction: Real-time adjustment for processing delays
- External Audio Sources: Integration with professional mixing consoles
- Multi-Language Support: Simultaneous audio track encoding
- Audio Enhancement: Noise reduction and dynamic range optimization IPTV encoder.
Niche-Specific Recommendations:
Churches and Religious Organizations:
- Multi-camera switching integration
- Archive recording capabilities
- Social media streaming optimization
- Donation platform integration support
Esports and Gaming Venues:
- Ultra-low latency for competitive integrity
- Multiple game feed integration
- Spectator camera management
- Tournament bracket overlay support
Event Production Companies:
- Portable, ruggedized hardware designs
- Battery backup integration
- Wireless streaming capabilities
- Remote monitoring and control
IPTV Resellers and Service Providers:
- Scalable encoding farms
- Automated channel management
- Quality monitoring integration
- Billing system compatibility
Deployment Use Cases
Real-world IPTV encoder deployment scenarios demonstrate the versatility and impact of professional encoding solutions across diverse industries and applications.
IPTV Resellers and 24/7 Content Distribution: Service providers managing multiple channels require encoding solutions that deliver consistent quality while minimizing operational overhead. Successful deployments feature:
- Redundant Encoding Arrays: Multiple encoders per channel for failover protection
- Centralized Management: Single interface controlling dozens of encoding units
- Quality Monitoring: Automated alerts for stream degradation or failures
- Bandwidth Optimization: Dynamic bitrate adjustment based on network conditions IPTV encoder.
Case study: A regional IPTV provider reduced customer complaints by 75% after upgrading from software-based encoding to dedicated hardware units, improving stream stability during peak viewing hours.
Live Sports Broadcasting: Sports streaming demands ultra-reliable performance with zero tolerance for failures during critical moments:
- Multi-Camera Integration: Seamless switching between field cameras and commentary feeds
- Instant Replay Capabilities: Integration with video production systems
- Mobile Streaming Optimization: Dedicated streams for mobile viewers
- Social Media Integration: Highlight clips for Twitter and Instagram
Hospitality Industry Applications: Hotels, bars, and entertainment venues leverage IPTV encoders for enhanced guest experiences:
- Local Content Integration: Community events and promotional content
- Multi-Language Support: International guest accommodation
- Interactive Services: Menu integration and local information
- Revenue Generation: Advertising insertion capabilities
Educational Institution Deployments: Schools and universities utilize encoding technology for distance learning and campus communications:
- Lecture Capture: Automated recording and streaming of classroom sessions
- Campus Events: Graduation ceremonies and sporting events
- Emergency Communications: Campus-wide alert distribution
- Multi-Campus Connectivity: Shared resources across geographic locations
Creative Deployment Example: Drone-to-IPTV Integration: Innovative use case: Aerial event coverage using drone-mounted cameras streaming directly to IPTV servers:
- Real-Time Aerial Footage: Unique perspectives for outdoor events
- Wireless Integration: 4G/5G connectivity for remote locations
- Stabilization Processing: Smooth footage despite aircraft movement
- Multi-Destination Streaming: Simultaneous broadcast and archive recording
This configuration enables event organizers to provide premium aerial coverage without expensive helicopter rentals or complex ground-based camera systems.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Professional IPTV encoder deployment success hinges on avoiding critical configuration and operational errors that can compromise streaming quality and reliability. IPTV encoder.
Protocol Selection Errors: Many operators select streaming protocols based on familiarity rather than application requirements. Common mistakes include:
- Using RTMP for Low-Latency Applications: RTMP inherently introduces 3-10 seconds of delay
- Ignoring Protocol Compatibility: Some devices don’t support modern protocols like HLS
- Overlooking Network Infrastructure: Multicast protocols require proper switch configuration
- Fix: Match protocol selection to specific latency and compatibility requirements
Firmware Update Negligence: Outdated encoder firmware leads to security vulnerabilities and performance limitations:
- Security Risks: Unpatched vulnerabilities expose networks to attacks
- Feature Limitations: Missing codec support and optimization improvements
- Compatibility Issues: Problems with newer streaming platforms and protocols
- Fix: Implement scheduled firmware update procedures and test in non-production environments
Bitrate Overload Mistakes: Excessive bitrate configuration causes network congestion and viewer buffering:
- Network Capacity Ignorance: Exceeding available upload bandwidth
- Viewer Connection Assumptions: Not considering audience internet speeds
- Mobile Optimization Failure: Desktop-optimized streams perform poorly on mobile
- Fix: Implement adaptive bitrate streaming and monitor network utilization metrics
Audio Configuration Oversights: Audio problems often receive less attention than video issues but significantly impact viewer experience:
- Sample Rate Mismatches: Incompatible audio formats cause playback issues
- Channel Configuration Errors: Stereo content encoded as mono or vice versa
- Synchronization Problems: Audio/video timing misalignment
- Fix: Standardize audio configurations and implement monitoring for sync issues
Cooling and Environmental Neglect: Hardware encoders require proper environmental conditions for reliable operation:
- Inadequate Ventilation: Overheating causes performance throttling and failures
- Dusty Environments: Accumulated debris blocks cooling systems
- Temperature Monitoring Absence: No alerts for thermal issues
- Fix: Install encoders in climate-controlled environments with regular maintenance schedules
Real-World Experience Fixes: Based on field deployments across hundreds of installations:
- Power Protection: UPS systems prevent stream interruptions during power fluctuations
- Network Redundancy: Dual internet connections with automatic failover
- Monitoring Integration: Centralized alerting for proactive issue resolution
- Documentation Standards: Detailed configuration records for rapid troubleshooting
Maintenance & Long-Term Storage
Proper IPTV encoder maintenance extends equipment lifespan and ensures consistent streaming performance throughout the device’s operational life. Professional maintenance protocols minimize downtime and protect technology investments.
Thermal Management Best Practices: Heat represents the primary threat to encoder reliability and performance. Implementing comprehensive cooling strategies prevents thermal-related failures:
- Regular Vent Cleaning: Monthly cleaning prevents dust accumulation that blocks airflow
- Temperature Monitoring: Continuous thermal monitoring with automated alerts
- Environment Control: Maintain ambient temperatures below 75°F (24°C) for optimal performance
- Airflow Optimization: Ensure adequate clearance around ventilation ports
Storage Environment Requirements: Long-term storage conditions significantly impact equipment reliability when units return to service:

- Humidity Control: Store in environments with 30-50% relative humidity
- Temperature Stability: Avoid extreme temperature fluctuations that stress components
- Dust Protection: Use protective covers or clean storage enclosures
- Corrosion Prevention: Anti-static bags for sensitive electronic components
Firmware Update Procedures: Systematic firmware management prevents security vulnerabilities and ensures access to latest features:
- Backup Configurations: Save current settings before firmware updates
- Staged Updates: Test firmware in non-production environments first
- Version Documentation: Maintain records of firmware versions across device fleet
- Rollback Procedures: Establish protocols for reverting problematic updates
Configuration Backup Strategies: Equipment failures become minor inconveniences rather than major disasters with proper backup procedures:
- Automated Backups: Schedule regular configuration exports
- Cloud Storage: Store backups in geographically diverse locations
- Version Control: Maintain historical configurations for comparison and rollback
- Recovery Testing: Periodically verify backup restoration procedures
Preventive Maintenance Schedules: Proactive maintenance prevents emergency repairs and extends equipment lifespan:
Monthly Tasks:
- Clean air vents and cooling fans
- Verify network connectivity and streaming health
- Update streaming platform credentials if expired
- Review error logs for recurring issues
Quarterly Tasks:
- Comprehensive cleaning of internal components
- Firmware update evaluation and planning
- Performance benchmark testing
- Configuration backup verification
Annual Tasks:
- Professional calibration and alignment
- Hardware inspection for component wear
- Network security audit and updates
- Replacement planning for aging equipment
Conclusion
Professional IPTV encoder selection fundamentally determines streaming success in today’s competitive digital landscape. The five encoder categories we’ve examined—from entry-level units perfect for small venues to enterprise-grade systems handling mission-critical broadcasts—offer solutions for every application and budget. Remember that the best encoder combines technical specifications with operational reliability, providing consistent performance that keeps viewers engaged and coming back for more. IPTV encoder.
Success with IPTV encoding extends beyond hardware selection to encompass proper setup procedures, ongoing maintenance, and strategic optimization for specific use cases. Whether you’re an IPTV reseller managing multiple channels, a church broadcasting services to remote congregations, or an event producer delivering live content, the right encoder becomes the foundation upon which your entire streaming strategy builds.
Ready to future-proof your IPTV broadcast? Invest in a reliable IPTV encoder today—drop your questions in the comments or subscribe for more reviews and technical insights that help you make informed streaming technology decisions.
FAQs
Q1: What’s the difference between an IPTV encoder and transcoder? An IPTV encoder converts raw video signals (HDMI, SDI) into compressed digital streams for network transmission. A transcoder converts already-encoded video from one format to another (e.g., H.264 to H.265) without accessing raw video signals. Encoders handle live video sources, while transcoders work with existing video files or streams.
Q2: Can one encoder stream to multiple platforms simultaneously? Yes, professional IPTV encoders support multi-destination streaming, allowing simultaneous broadcast to YouTube Live, Facebook, custom IPTV servers, and other platforms. However, bandwidth requirements multiply with each additional destination, so ensure adequate network capacity for multiple concurrent streams. IPTV encoder.
Q3: Do IPTV encoders support 4K resolution streaming? Modern professional encoders increasingly support 4K encoding, though this requires significantly more processing power and bandwidth. Entry-level units typically max out at 1080p, while enterprise-grade encoders handle 4K at 60fps. Consider H.265 encoding for 4K applications to reduce bandwidth requirements by approximately 40-50%.
Q4: What’s the best IPTV encoder for beginners? For beginners, look for encoders with web-based configuration interfaces, automatic network setup (DHCP), and preset encoding profiles for popular streaming platforms. Entry-level hardware encoders offer better reliability than software solutions while maintaining user-friendly operation. Prioritize units with good technical support and comprehensive documentation for learning purposes.





