Introduction: Why Encoder IPTV Mistakes Can Cost You in 2025
An Encoder IPTV is the backbone of any high-quality streaming setup, and mistakes can be costly—leading to viewer dropouts, revenue losses, and damaged reputation. As streaming demand continues to surge in 2025, Encoder IPTV providers, broadcasters, and content creators face increasing pressure to deliver flawless live streaming experiences. Yet many professionals unknowingly make critical errors that compromise their entire streaming infrastructure.
The consequences of Encoder IPTV mistakes extend far beyond technical hiccups. A single misconfiguration can result in buffering issues for thousands of viewers, while poor Encoder IPTV planning can leave you scrambling during peak viewing hours. Whether you’re managing a small operation or broadcasting to millions, understanding these common pitfalls—and how to avoid them—is essential for maintaining viewer satisfaction and business continuity.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore seven critical mistakes that can devastate your streaming performance and provide actionable solutions to protect your investment. From real-time encoding issues to long-term scalability challenges, you’ll discover how to build a robust streaming infrastructure that stands the test of time.
Table of Contents
How Encoder IPTV Works: Understanding the Basics
Before diving into common mistakes, it’s crucial to understand how an functions within your streaming ecosystem. At its core, an Encoder IPTV device captures raw video signals from cameras, satellite feeds, or other sources and converts them into compressed digital formats suitable for internet distribution.
The Encoding Process Explained
The encoding workflow involves several critical steps:
Video Signal Capture: The encoder receives uncompressed video signals through various input methods—HDMI, SDI, composite, or IP-based sources. This raw footage contains massive amounts of data that must be processed in real-time.
Compression and Processing: Using advanced algorithms like H.264, H.265 (HEVC), or AV1, the encoder compresses video data while maintaining acceptable quality levels. This process includes resolution scaling, frame rate optimization, and bitrate configuration to match your streaming requirements.
Multi-Protocol Broadcast: Modern encoders support multiple output protocols simultaneously, including RTMP for social platforms, HLS for mobile devices, and SRT for ultra-low latency streaming. This versatility allows broadcasters to reach audiences across different platforms without multiple encoding setups.
Common Challenges in Encoding Workflows
Professional streaming faces unique technical challenges that can derail even well-planned broadcasts. Real-time encoding demands significant processing power, and any bottleneck can cause frame drops or audio synchronization issues. Network instability, power fluctuations, and Encoder IPTV hardware limitations all contribute to potential failure points that require careful planning and monitoring.
Understanding these fundamentals helps identify why certain Encoder IPTV mistakes prove so costly. When Encoder IPTV systems fail, the entire streaming chain collapses, making prevention far more valuable than reactive troubleshooting.
Top 7 Critical Mistakes Broadcasters Make with Encoder IPTV
Mistake 1: Not Testing Your Encoder IPTV in Real Conditions
The most devastating error broadcasters make is deploying Encoder IPTV systems without comprehensive real-world testing. Laboratory conditions rarely mirror the complexities of live broadcasting environments, where network congestion, temperature fluctuations, and unexpected signal variations create perfect storms for failure.

Why This Happens: Many teams rush to go live without adequate testing phases, often due to tight deadlines or overconfidence in Encoder IPTV manufacturer specifications. Others test only basic functionality without simulating peak load conditions or extended operation periods.
The Real Cost: A major sports broadcaster learned this lesson the hard way when their untested setup failed during a championship match, resulting in a 47-minute outage that affected 2.3 million viewers. The incident cost them $780,000 in advertising refunds and damaged relationships with key sponsors.
The Fix: Implement a comprehensive testing protocol that includes:
- Stress testing under maximum expected load
- Extended duration tests running 24-48 hours continuously
- Network variation simulation with bandwidth throttling and packet loss
- Temperature cycling to verify performance across environmental conditions
- Failover testing to ensure backup systems activate properly
Document all test results and create baseline performance metrics for ongoing monitoring. Never deploy an Encoder IPTV configuration that hasn’t been validated under conditions matching or exceeding your production environment.
Mistake 2: Skipping Firmware and Security Updates
Firmware neglect represents one of the most preventable yet common Encoder IPTV failures. Many broadcasters treat devices like set-and-forget appliances, ignoring critical updates that address security vulnerabilities, performance improvements, and compatibility issues.
The Security Risk: Outdated Encoder IPTV firmware creates entry points for cyberattacks that can compromise entire streaming networks. In 2024, security researchers identified vulnerabilities in popular Encoder IPTV models that allowed remote code execution—attacks that could only be prevented through timely firmware updates.
Performance Impact: Manufacturers continuously optimize encoding algorithms, fix memory leaks, and enhance protocol compatibility. Skipping updates means missing out on performance improvements that could reduce bandwidth costs and improve viewer experience.
The Solution: Establish a systematic update management process:
- Monitor manufacturer notifications for security bulletins and firmware releases
- Test updates in staging environments before production deployment
- Schedule maintenance windows for updates during low-traffic periods
- Maintain update logs tracking firmware versions and change histories
- Implement automated monitoring to detect when devices fall behind update schedules
Create redundant systems that allow for rolling updates without service interruption. Never update critical Encoder IPTV systems during peak viewing periods or major events.
Mistake 3: Overcomplicating Your Encoder IPTV Setup with Unnecessary Features
Feature creep destroys encoder reliability faster than almost any other factor. Modern live streaming encoders offer impressive capabilities, but activating every available feature often introduces instability, increases resource consumption, and complicates troubleshooting.
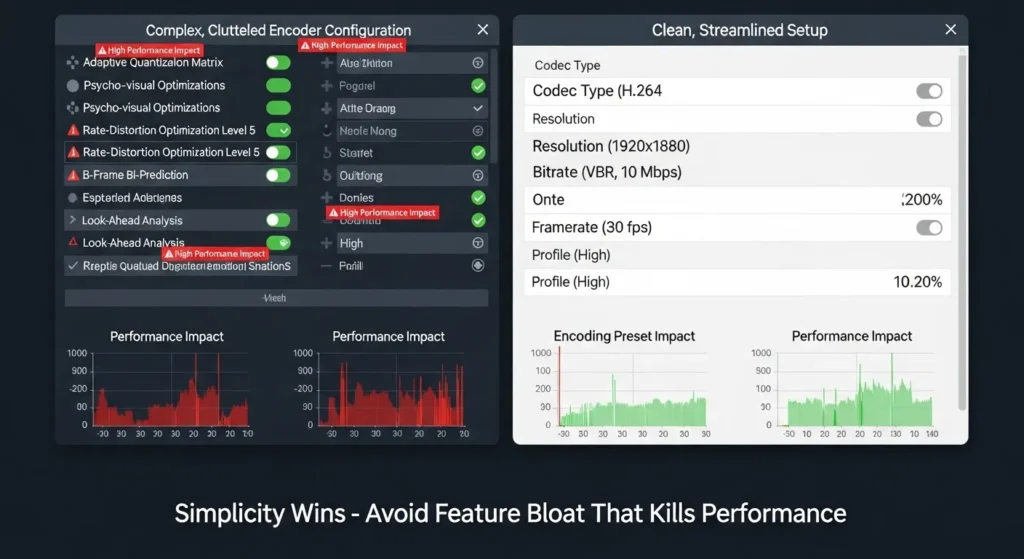
Common Overcomplications Include:
- Enabling multiple simultaneous transcoding profiles when single-profile solutions suffice
- Activating advanced video processing features that provide minimal viewer benefit
- Implementing complex audio mixing when simple pass-through works better
- Using proprietary protocols when standard options offer better compatibility
The Performance Penalty: Each additional feature consumes CPU cycles, memory, and network resources. A broadcaster running 12 simultaneous output profiles experienced frequent crashes until they streamlined to 4 essential profiles, resulting in 99.7% uptime improvement.
Simplification Strategy:
- Audit current configurations and identify truly necessary features
- Benchmark performance with minimal configurations first
- Add complexity incrementally while monitoring stability metrics
- Document the purpose of each enabled feature for future reviews
- Regular configuration reviews to eliminate unused features
Focus on core requirements: reliable video capture, efficient compression, and stable output delivery. Advanced features should only be enabled when they solve specific, measurable problems.
Mistake 4: Ignoring Redundancy and Backup Options
Single-point-of-failure configurations represent catastrophic risks that many broadcasters don’t recognize until disaster strikes. Stream redundancy isn’t optional for professional operations—it’s essential insurance against inevitable hardware failures.
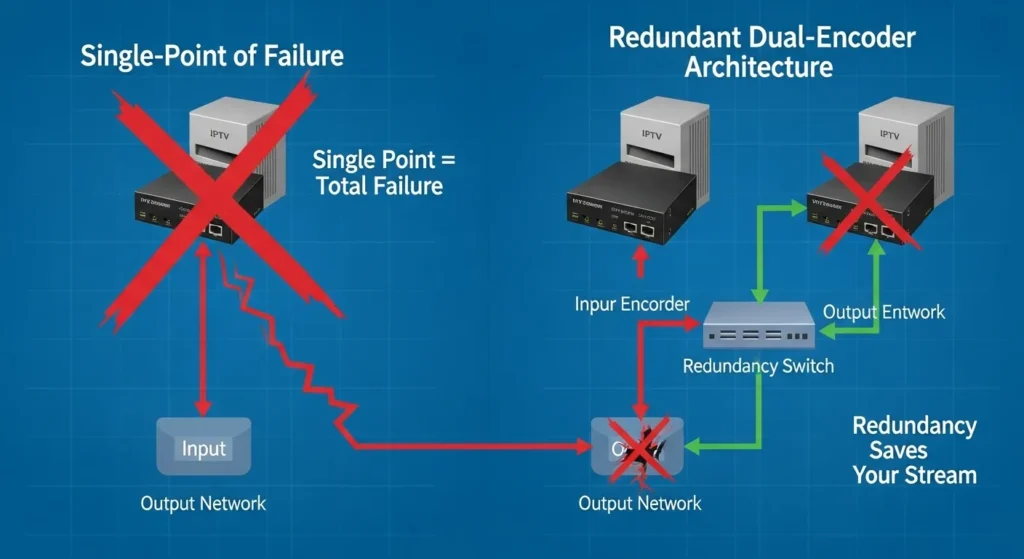
Real-World Consequences: A live news broadcaster lost 3 hours of coverage during breaking news when their primary encoder failed and no backup system existed. The incident resulted in significant audience loss to competitors and regulatory scrutiny from broadcasting authorities.
Redundancy Implementation Levels:
Basic Level: Hot-standby Encoder IPTV units with manual switchover capabilities Intermediate Level: Automatic Encoder IPTV failover systems with health monitoring Advanced Level: Load-balanced Encoder IPTV clusters with seamless transitions Enterprise Level: Geographically distributed encoding with disaster recovery
Building Effective Redundancy:
- Duplicate critical components including encoders, network switches, and power supplies
- Implement monitoring systems that detect failures within seconds
- Test failover procedures regularly under various failure scenarios
- Document recovery procedures with step-by-step instructions
- Train multiple team members on emergency response protocols
Never rely on single devices for mission-critical streams. The cost of redundancy pales in comparison to the revenue and reputation damage from extended outages.
Mistake 5: Underestimating Cooling and Environmental Requirements
Environmental factors destroy more Encoder IPTV systems than most broadcasters realize. Video signal capture and real-time compression generate significant heat, and inadequate cooling leads to thermal throttling, component degradation, and premature Encoder IPTV hardware failure.
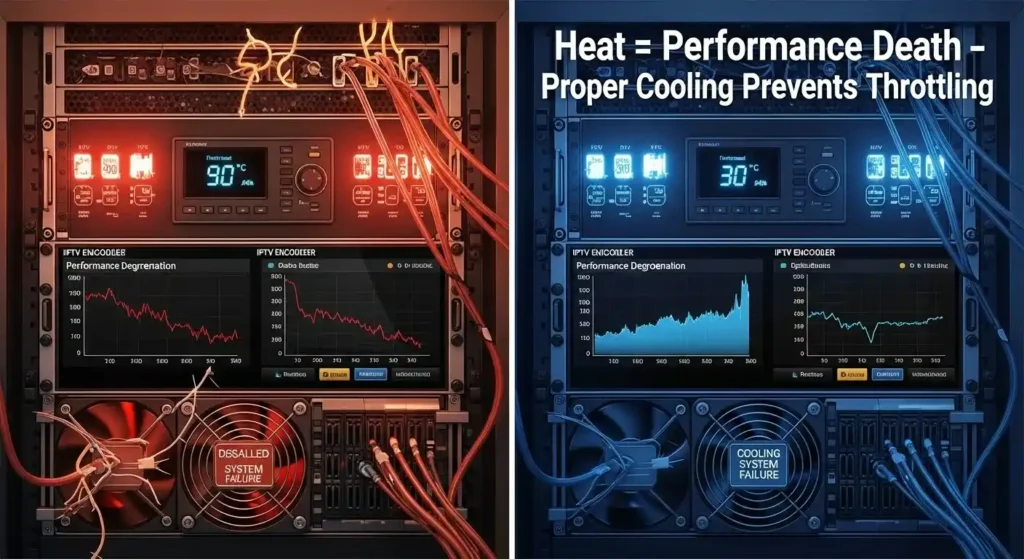
Temperature Impact on Performance: Encoder IPTV performance degrades predictably as temperatures rise. At 85°F (29°C), most Encoder IPTV units begin thermal throttling. At 95°F (35°C), many units experience critical failures. Yet many installations ignore these thermal requirements entirely.
Common Environmental Mistakes:
- Installing Encoder IPTV units in poorly ventilated rack spaces
- Blocking airflow with cables or adjacent equipment
- Ignoring humidity control in Encoder IPTV equipment rooms
- Failing to account for heat generated by multiple devices
- Using inadequate air conditioning systems during summer months
Environmental Best Practices:
- Maintain temperatures between 65-75°F (18-24°C) in equipment areas
- Ensure adequate airflow with minimum 3 inches clearance around ventilation ports
- Monitor humidity levels keeping them between 45-55% relative humidity
- Install temperature sensors with alerting systems for early warning
- Plan HVAC redundancy to prevent cooling system failures
Regular thermal monitoring prevents costly Encoder IPTV hardware replacements and maintains consistent encoding performance. Invest in proper environmental controls as essential infrastructure, not optional extras.
Mistake 6: Choosing an Encoder IPTV Device Without Long-Term Support
Short-sighted Encoder IPTV selection decisions create expensive problems years later when manufacturers discontinue support, stop providing updates, or exit the market entirely. Many broadcasters focus exclusively on initial purchase price while ignoring total cost of ownership.
The Hidden Costs of Poor Support:
- Inability to address security vulnerabilities in aging firmware
- Lack of technical support when critical issues arise
- Incompatibility with newer streaming protocols and standards
- Forced premature Encoder IPTV replacements when support ends
- Higher maintenance costs for unsupported Encoder IPTV equipment
Evaluating Manufacturer Support Quality:
- Research company history and financial stability
- Review support policies including warranty terms and update commitments
- Assess documentation quality and technical resource availability
- Test customer support responsiveness before major purchases
- Examine user communities and third-party support options
Long-Term Planning Considerations:
- Choose Encoder IPTV manufacturers with proven 5+ year support commitments
- Verify backward compatibility policies for Encoder IPTV firmware updates
- Understand end-of-life migration pathways for current products
- Budget for regular Encoder IPTV equipment refresh cycles every 3-5 years
- Maintain relationships with multiple vendors to avoid single-source dependency
Strategic vendor selection protects long-term Encoder IPTV investments and ensures continued access to critical support resources throughout the product lifecycle.
Mistake 7: Failing to Plan for Future Scaling Needs
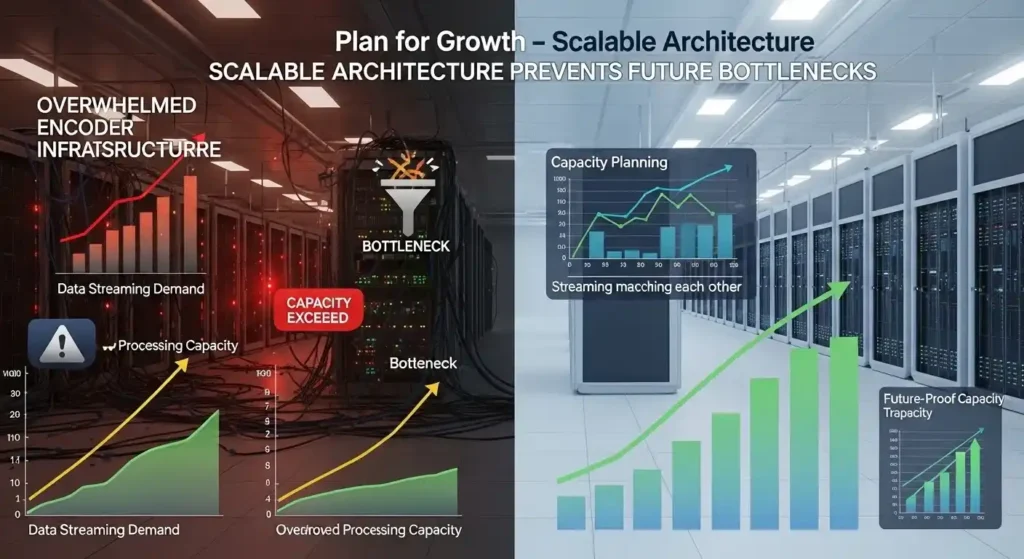
Scalability oversights force expensive infrastructure overhauls when demand exceeds capacity. Many broadcasters design IPTV setup guides around current requirements without considering growth trajectories, new protocol adoption, or changing viewer expectations.
Common Scaling Bottlenecks:
- Processing limitations that prevent handling additional streams
- Network capacity constraints affecting bitrate configuration flexibility
- Storage limitations for recording and time-shifting capabilities
- Power and cooling limitations restricting equipment additions
- Licensing restrictions that increase costs with channel expansion
Scaling Planning Framework:
Short-term (6-12 months): Plan for 50-100% capacity increases Medium-term (1-3 years): Consider new format support (4K, HDR, VR) Long-term (3-5 years): Evaluate platform migration and technology refresh needs
Future-Proofing Strategies:
- Choose modular architectures that support incremental expansion
- Implement software-defined solutions with flexible licensing models
- Design network infrastructure with 3-5x current bandwidth requirements
- Plan physical space for additional equipment installations
- Budget for technology transitions including staff training and migration costs
Ultra-low latency streaming demands will continue growing, requiring Encoder IPTV capabilities that many current deployments cannot support. Plan Encoder IPTV infrastructure investments around emerging requirements rather than just current needs.
How to Avoid Encoder IPTV Pitfalls
Preventing Encoder IPTV failures requires systematic approaches that address both technical and operational aspects of streaming infrastructure management. Success depends on implementing comprehensive monitoring, maintenance, and planning processes that catch Encoder IPTV problems before they affect viewers.
Testing and Monitoring Best Practices
Effective monitoring goes beyond basic uptime checks to include performance metrics that predict failures before they occur. Implement monitoring systems that track:
Performance Metrics: CPU utilization, memory usage, network throughput, encoding frame rates, and output bitrate stability Quality Metrics: Video quality scores, audio synchronization, packet loss rates, and viewer experience indicators
Environmental Metrics: Temperature, humidity, power consumption, and cooling system performance Security Metrics: Failed login attempts, unusual network activity, and configuration change tracking
Create automated alerting systems with escalating notification procedures. Critical alerts should reach on-call engineers within 30 seconds, while trending issues can be addressed during business hours.
Firmware and Security Update Schedules
Systematic update management prevents security vulnerabilities while maintaining system stability. Develop update policies that balance security needs with operational requirements:
Emergency Updates: Security patches deployed within 48 hours after testing Regular Updates: Feature and bug-fix releases deployed monthly during maintenance windows Major Updates: Annual or bi-annual updates requiring extended testing and possible configuration changes
Maintain staging environments that mirror production setups for update testing. Never deploy untested updates to critical systems, regardless of urgency.
Proper Planning for Redundancy and Growth
Infrastructure planning must account for both immediate resilience needs and long-term expansion requirements. Design systems with built-in redundancy at every level:
Network Redundancy: Multiple internet connections from different providers Power Redundancy: UPS systems and backup generators for extended outages Equipment Redundancy: Hot-standby encoders with automatic failover capabilities Geographic Redundancy: Backup facilities in different locations for disaster recovery
Plan expansion paths that minimize service disruption during growth phases. Modular architectures support incremental scaling without complete system overhauls.
Recommended Encoder IPTV Models for Reliable Streaming in 2025
Choosing appropriate hardware significantly impacts long-term success and operational costs. Current market offerings span from budget-friendly Encoder IPTV solutions suitable for small operations to enterprise-grade Encoder IPTV systems capable of handling massive concurrent streams.
Budget-Friendly Options ($200–$800)
Entry-level Encoder IPTV units serve small IPTV operations, churches, schools, and content creators building audience bases. While feature-limited, quality units in this range provide reliable SRT / HLS / RTMP output for basic streaming needs.
Key Features to Prioritize:
- H.264 hardware encoding with at least 1080p60 capability
- Multiple output protocols including RTMP, HLS, and UDP
- Web-based configuration interfaces for remote management
- HDMI and SDI input options for professional cameras
- Firmware update capabilities with manufacturer support commitments
Budget Encoder IPTV units work well for single-channel operations or backup systems in larger deployments. Avoid Encoder IPTV units without update capabilities or from manufacturers with poor support records.
Professional-Grade Units ($800–$3,000)
Mid-range systems handle multiple simultaneous streams while offering advanced features like redundant inputs, hardware-accelerated transcoding, and professional monitoring capabilities. These Encoder IPTV units serve regional broadcasters, corporate streaming, and medium-scale IPTV operations.
Advanced Capabilities Include:
- Multiple encoding profiles with simultaneous outputs
- Redundant input switching for automatic source failover
- Advanced audio processing with mixing and delay compensation
- SNMP monitoring integration with network management systems
- API control for automated configuration and monitoring
Professional Encoder IPTV systems typically offer 3-5 year manufacturer support with regular firmware updates and technical assistance. Choose Encoder IPTV models with proven reliability records and active user communities.
Enterprise Solutions ($3,000+)
High-end Encoder IPTV systems support large-scale operations with features like clustered deployment, advanced redundancy, and carrier-grade reliability. These systems serve major broadcasters, telecommunications providers, and large IPTV operators managing hundreds of channels.
Enterprise Features:
- Clustered operation with load balancing and automatic failover
- Advanced security including encryption, authentication, and access control
- Comprehensive APIs for integration with broadcast automation systems
- Hot-swappable components for maintenance without service interruption
- 24/7 manufacturer support with guaranteed response times
Enterprise solutions require significant technical expertise for deployment and ongoing management. Factor professional services costs into total project budgets when evaluating these Encoder IPTV systems.
Conclusion: Protect Your Streaming Quality with Encoder IPTV Best Practices
The seven critical mistakes outlined in this guide represent the most common—and most costly— errors that can devastate streaming operations in 2025. From inadequate testing procedures to poor long-term Encoder IPTV planning, these pitfalls affect broadcasters of all sizes and experience levels. However, understanding these challenges provides the foundation for building resilient, scalable streaming infrastructure that delivers consistent viewer experiences.

Encoder IPTV success requires more than just selecting quality hardware—it demands systematic approaches to testing, monitoring, maintenance, and growth planning. The broadcasters who thrive in 2025’s competitive streaming landscape will be those who invest in proper Encoder IPTV infrastructure design, maintain vigilant operational practices, and plan for long-term scalability from day one.
Remember that streaming reliability directly impacts viewer satisfaction, advertiser confidence, and revenue generation. The costs associated with implementing Encoder IPTV best practices pale in comparison to the financial and reputational damage caused by streaming failures during critical moments. Whether you’re managing a small operation or broadcasting to millions of viewers, these principles provide the framework for sustainable streaming success.
Take action today by auditing your current Encoder IPTV setup against these seven critical mistakes. Document identified risks, prioritize fixes based on potential impact, and develop systematic processes that prevent future Encoder IPTV problems. Your viewers—and your bottom line—will benefit from the investment in proper infrastructure and operational practices.





